Summary: Renamed shaders to be prefixed with Hard/Soft depending on if they use a probabalistic blending (Soft) or use the closest face (Hard). There is some code duplication but I thought it would be cleaner to have separate shaders for each task rather than: - inheritance (which we discussed previously that we want to avoid) - boolean (hard/soft) or a string (hard/soft) - new blending functions other than the ones provided would need if statements in the current shaders which might get messy. Also added a `flat_shading` function and a `FlatShader` - I could make this into a tutorial as it was really easy to add a new shader and it might be a nice showcase. NOTE: There are a few more places where the naming will need to change (e.g the tutorials) but I wanted to reach a consensus on this before changing it everywhere. Reviewed By: jcjohnson Differential Revision: D19761036 fbshipit-source-id: f972f6530c7f66dc5550b0284c191abc4a7f6fc4

Introduction
PyTorch3d provides efficient, reusable components for 3D Computer Vision research with PyTorch.
Key features include:
- Data structure for storing and manipulating triangle meshes
- Efficient operations on triangle meshes (projective transformations, graph convolution, sampling, loss functions)
- A differentiable mesh renderer
PyTorch3d is designed to integrate smoothly with deep learning methods for predicting and manipulating 3D data. For this reason, all operators in PyTorch3d:
- Are implemented using PyTorch tensors
- Can handle minibatches of hetereogenous data
- Can be differentiated
- Can utilize GPUs for acceleration
Within FAIR, PyTorch3d has been used to power research projects such as Mesh R-CNN.
Installation
For detailed instructions refer to INSTALL.md.
License
PyTorch3d is released under the BSD-3-Clause License.
Tutorials
Get started with PyTorch3d by trying one of the tutorial notebooks.
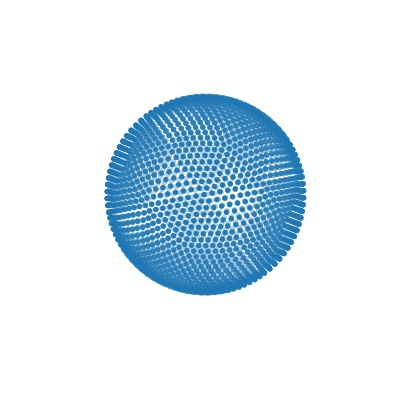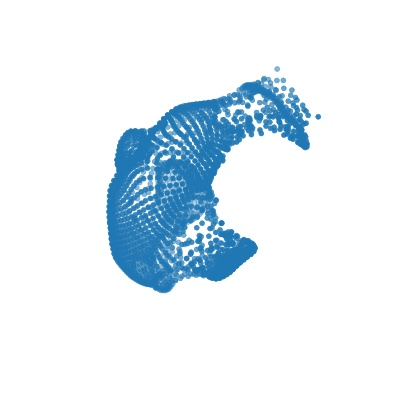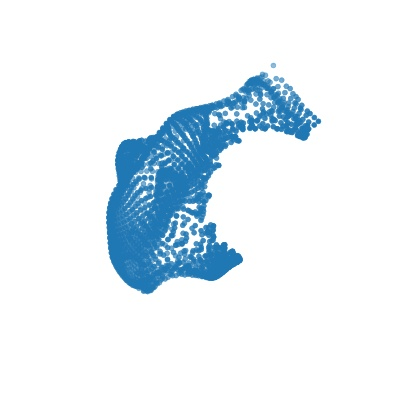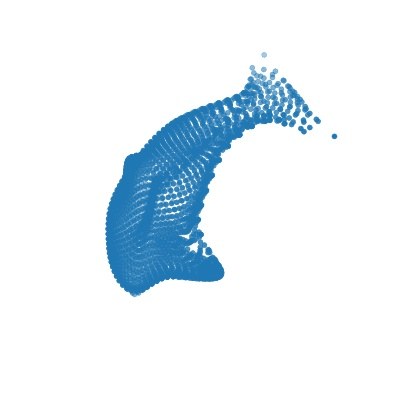 |
 |
|---|---|
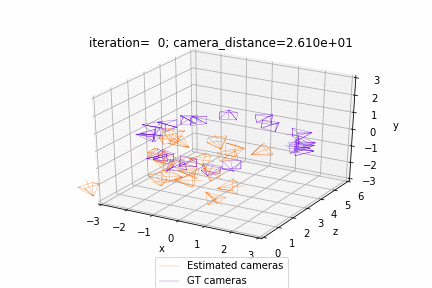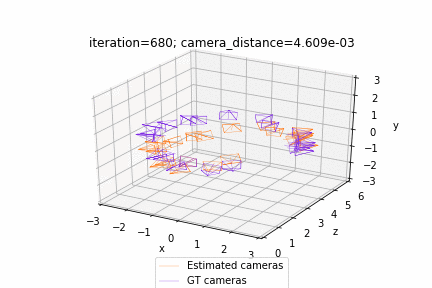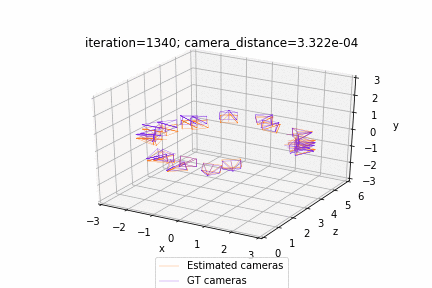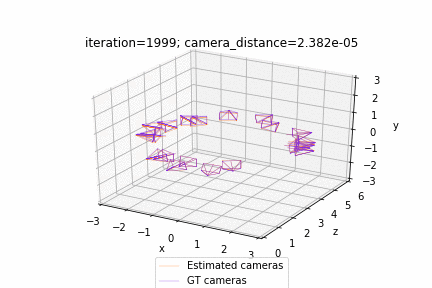
| Deform a sphere mesh to dolphin | Bundle adjustment |
 |
 |
|---|---|
| Render textured meshes | Camera position optimization |
Documentation
Learn more about the API by reading the PyTorch3d documentation.
We also have deep dive notes on several API components:
Development
We welcome new contributions to Pytorch3d and we will be actively maintaining this library! Please refer to CONTRIBUTING.md for full instructions on how to run the code, tests and linter, and submit your pull requests.
Contributors
PyTorch3d is written and maintained by the Facebook AI Research Computer Vision Team.
Citation
If you find PyTorch3d useful in your research, please cite:
@misc{ravi2020pytorch3d,
author = {Nikhila Ravi and Jeremy Reizenstein and David Novotny and Taylor Gordon
and Wan-Yen Lo and Justin Johnson and Georgia Gkioxari},
title = {PyTorch3D},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/facebookresearch/pytorch3d}},
year = {2020}
}