Summary: The iterative closest point algorithm - point-to-point version. Output of `bm_iterative_closest_point`: Argument key: `batch_size dim n_points_X n_points_Y use_pointclouds` ``` Benchmark Avg Time(μs) Peak Time(μs) Iterations -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- IterativeClosestPoint_1_3_100_100_False 107569 111323 5 IterativeClosestPoint_1_3_100_1000_False 118972 122306 5 IterativeClosestPoint_1_3_1000_100_False 108576 110978 5 IterativeClosestPoint_1_3_1000_1000_False 331836 333515 2 IterativeClosestPoint_1_20_100_100_False 134387 137842 4 IterativeClosestPoint_1_20_100_1000_False 149218 153405 4 IterativeClosestPoint_1_20_1000_100_False 414248 416595 2 IterativeClosestPoint_1_20_1000_1000_False 374318 374662 2 IterativeClosestPoint_10_3_100_100_False 539852 539852 1 IterativeClosestPoint_10_3_100_1000_False 752784 752784 1 IterativeClosestPoint_10_3_1000_100_False 1070700 1070700 1 IterativeClosestPoint_10_3_1000_1000_False 1164020 1164020 1 IterativeClosestPoint_10_20_100_100_False 374548 377337 2 IterativeClosestPoint_10_20_100_1000_False 472764 476685 2 IterativeClosestPoint_10_20_1000_100_False 1457175 1457175 1 IterativeClosestPoint_10_20_1000_1000_False 2195820 2195820 1 IterativeClosestPoint_1_3_100_100_True 110084 115824 5 IterativeClosestPoint_1_3_100_1000_True 142728 147696 4 IterativeClosestPoint_1_3_1000_100_True 212966 213966 3 IterativeClosestPoint_1_3_1000_1000_True 369130 375114 2 IterativeClosestPoint_10_3_100_100_True 354615 355179 2 IterativeClosestPoint_10_3_100_1000_True 451815 452704 2 IterativeClosestPoint_10_3_1000_100_True 511833 511833 1 IterativeClosestPoint_10_3_1000_1000_True 798453 798453 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ``` Reviewed By: shapovalov, gkioxari Differential Revision: D19909952 fbshipit-source-id: f77fadc88fb7c53999909d594114b182ee2a3def

Introduction
PyTorch3D provides efficient, reusable components for 3D Computer Vision research with PyTorch.
Key features include:
- Data structure for storing and manipulating triangle meshes
- Efficient operations on triangle meshes (projective transformations, graph convolution, sampling, loss functions)
- A differentiable mesh renderer
PyTorch3D is designed to integrate smoothly with deep learning methods for predicting and manipulating 3D data. For this reason, all operators in PyTorch3D:
- Are implemented using PyTorch tensors
- Can handle minibatches of hetereogenous data
- Can be differentiated
- Can utilize GPUs for acceleration
Within FAIR, PyTorch3D has been used to power research projects such as Mesh R-CNN.
Installation
For detailed instructions refer to INSTALL.md.
License
PyTorch3D is released under the BSD-3-Clause License.
Tutorials
Get started with PyTorch3D by trying one of the tutorial notebooks.
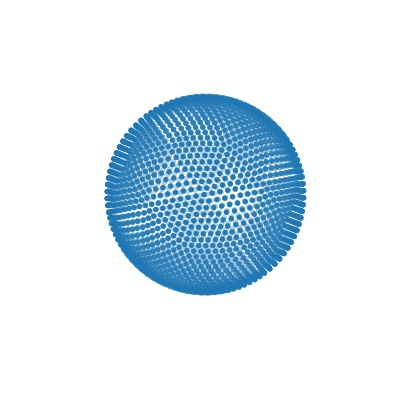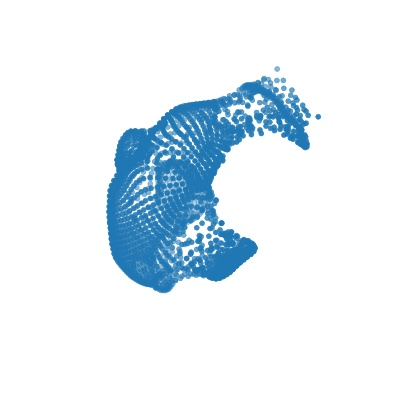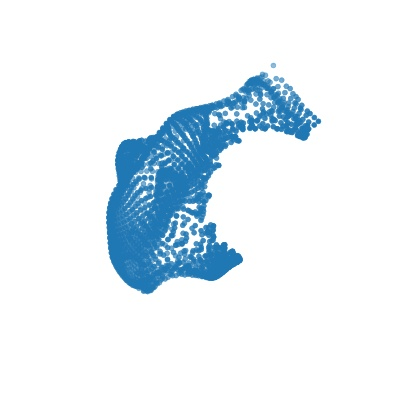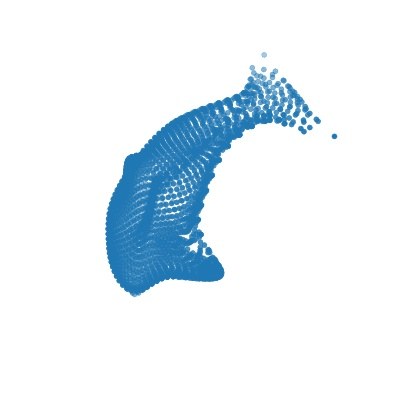 |
 |
|---|---|
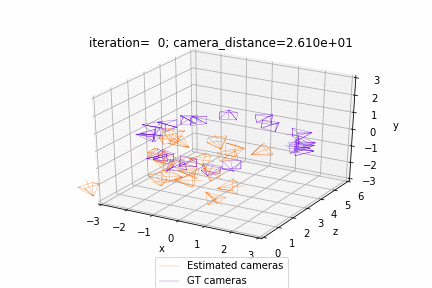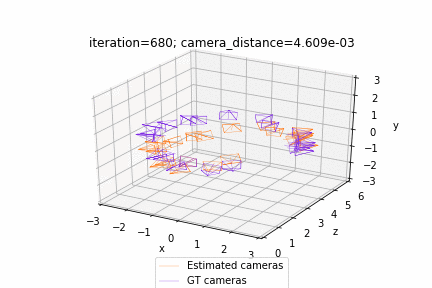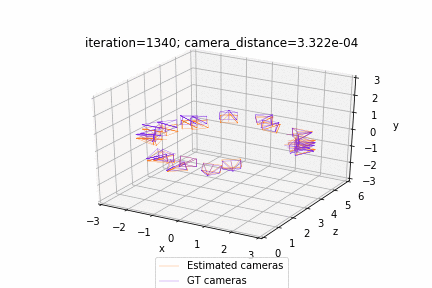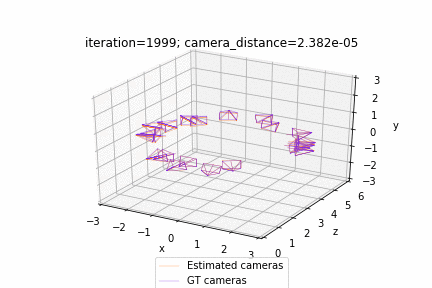
| Deform a sphere mesh to dolphin | Bundle adjustment |
 |
 |
|---|---|
| Render textured meshes | Camera position optimization |
Documentation
Learn more about the API by reading the PyTorch3D documentation.
We also have deep dive notes on several API components:
Development
We welcome new contributions to PyTorch3D and we will be actively maintaining this library! Please refer to CONTRIBUTING.md for full instructions on how to run the code, tests and linter, and submit your pull requests.
Contributors
PyTorch3D is written and maintained by the Facebook AI Research Computer Vision Team.
Citation
If you find PyTorch3D useful in your research, please cite:
@misc{ravi2020pytorch3d,
author = {Nikhila Ravi and Jeremy Reizenstein and David Novotny and Taylor Gordon
and Wan-Yen Lo and Justin Johnson and Georgia Gkioxari},
title = {PyTorch3D},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/facebookresearch/pytorch3d}},
year = {2020}
}