Summary: Support for moving all the tensors of the renderer to another device by calling `renderer.to(new_device)` Currently the `MeshRenderer`, `MeshRasterizer` and `SoftPhongShader` (and other shaders) are all of type `nn.Module` which already supports easily moving tensors of submodules (defined as class attributes) to a different device. However the class attributes of the rasterizer and shader (e.g. cameras, lights, materials), are of type `TensorProperties`, not nn.Module so we need to explicity create a `to` method to move these tensors to device. Note that the `TensorProperties` class already has a `to` method so we only need to call `cameras.to(device)` and don't need to worry about the internal tensors. The other option is of course making these other classes (cameras, lights etc) also of type nn.Module. Reviewed By: gkioxari Differential Revision: D23885107 fbshipit-source-id: d71565c442181f739de4d797076ed5d00fb67f8e

Introduction
PyTorch3D provides efficient, reusable components for 3D Computer Vision research with PyTorch.
Key features include:
- Data structure for storing and manipulating triangle meshes
- Efficient operations on triangle meshes (projective transformations, graph convolution, sampling, loss functions)
- A differentiable mesh renderer
PyTorch3D is designed to integrate smoothly with deep learning methods for predicting and manipulating 3D data. For this reason, all operators in PyTorch3D:
- Are implemented using PyTorch tensors
- Can handle minibatches of hetereogenous data
- Can be differentiated
- Can utilize GPUs for acceleration
Within FAIR, PyTorch3D has been used to power research projects such as Mesh R-CNN.
Installation
For detailed instructions refer to INSTALL.md.
License
PyTorch3D is released under the BSD-3-Clause License.
Tutorials
Get started with PyTorch3D by trying one of the tutorial notebooks.
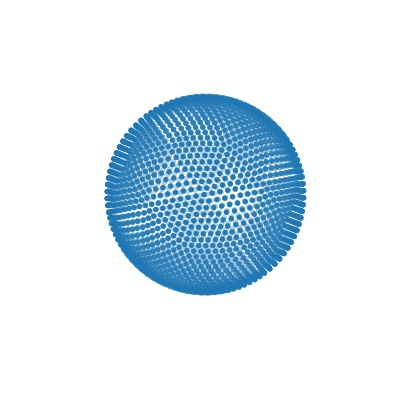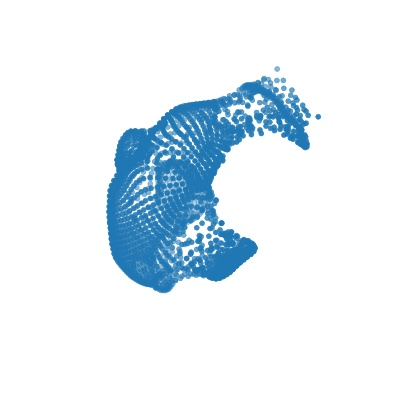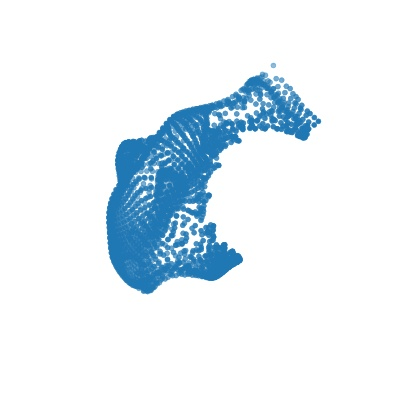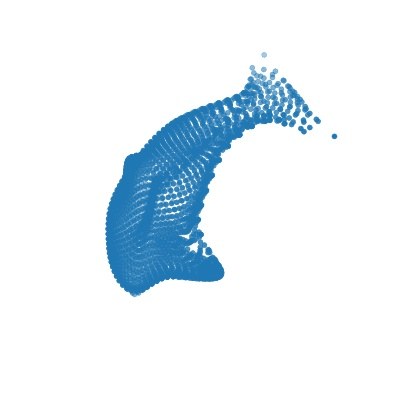 |
 |
|---|---|
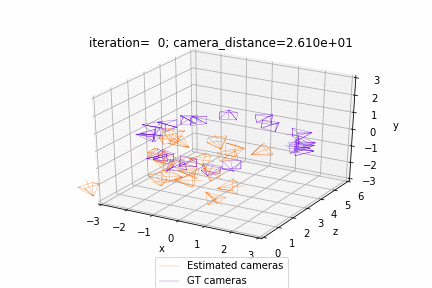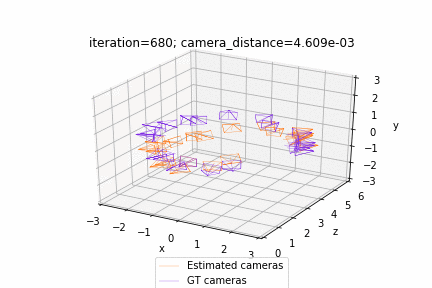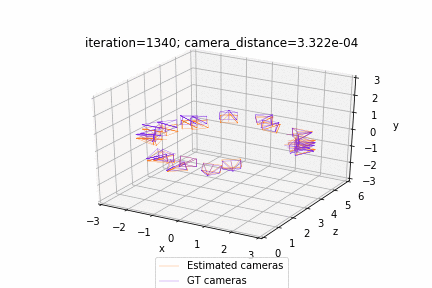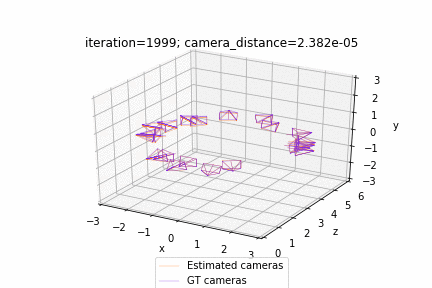
| Deform a sphere mesh to dolphin | Bundle adjustment |
 |
 |
|---|---|
| Render textured meshes | Camera position optimization |
Documentation
Learn more about the API by reading the PyTorch3D documentation.
We also have deep dive notes on several API components:
Overview Video
We have created a short (~14 min) video tutorial providing an overview of the PyTorch3D codebase including several code examples. Click on the image below to watch the video on YouTube:
Development
We welcome new contributions to PyTorch3D and we will be actively maintaining this library! Please refer to CONTRIBUTING.md for full instructions on how to run the code, tests and linter, and submit your pull requests.
Contributors
PyTorch3D is written and maintained by the Facebook AI Research Computer Vision Team.
Citation
If you find PyTorch3D useful in your research, please cite our tech report:
@article{ravi2020pytorch3d,
author = {Nikhila Ravi and Jeremy Reizenstein and David Novotny and Taylor Gordon
and Wan-Yen Lo and Justin Johnson and Georgia Gkioxari},
title = {Accelerating 3D Deep Learning with PyTorch3D},
journal = {arXiv:2007.08501},
year = {2020},
}
News
Please see below for a timeline of the codebase updates in reverse chronological order. We are sharing updates on the releases as well as research projects which are built with PyTorch3D. The changelogs for the releases are available under Releases, and the builds can be installed using conda as per the instructions in INSTALL.md.
[July 17th 2020]: PyTorch3D tech report published on ArXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.08501
[April 24th 2020]: PyTorch3D v0.2 released
[March 25th 2020]: SynSin codebase released using PyTorch3D: https://github.com/facebookresearch/synsin
[March 8th 2020]: PyTorch3D v0.1.1 bug fix release
[Jan 23rd 2020]: PyTorch3D v0.1 released. Mesh R-CNN codebase released: https://github.com/facebookresearch/meshrcnn
