mirror of
https://github.com/facebookresearch/pytorch3d.git
synced 2026-01-16 19:30:34 +08:00
screen cameras lose -1
Summary: All the renderers in PyTorch3D (pointclouds including pulsar, meshes, raysampling) use align_corners=False style. NDC space goes between the edges of the outer pixels. For a non square image with W>H, the vertical NDC space goes from -1 to 1 and the horizontal from -W/H to W/H. However it was recently pointed out that functionality which deals with screen space inside the camera classes is inconsistent with this. It unintentionally uses align_corners=True. This fixes that. This would change behaviour of the following: - If you create a camera in screen coordinates, i.e. setting in_ndc=False, then anything you do with the camera which touches NDC space may be affected, including trying to use renderers. The transform_points_screen function will not be affected... - If you call the function “transform_points_screen” on a camera defined in NDC space results will be different. I have illustrated in the diff how to get the old results from the new results but this probably isn’t the right long-term solution.. Reviewed By: gkioxari Differential Revision: D32536305 fbshipit-source-id: 377325a9137282971dcb7ca11a6cba3fc700c9ce
This commit is contained in:
committed by
 Facebook GitHub Bot
Facebook GitHub Bot
parent
cff4876131
commit
bf3bc6f8e3
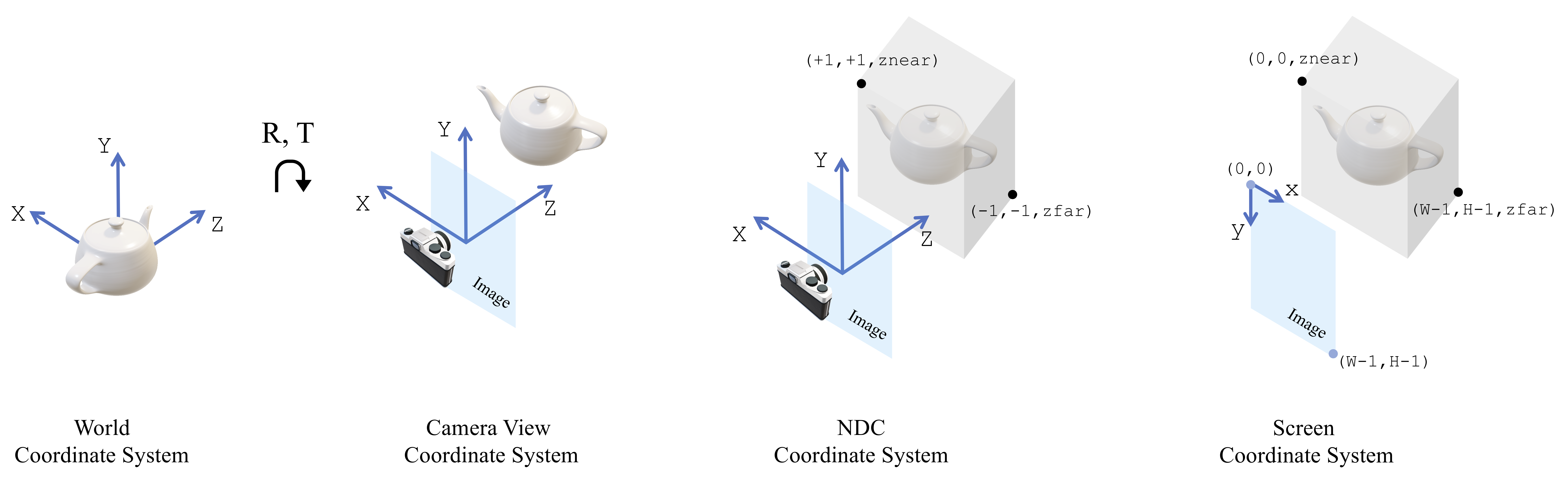
@@ -16,10 +16,11 @@ This is the system that has its origin on the image plane and the `Z`-axis perpe
|
|||||||
This is the normalized coordinate system that confines in a volume the rendered part of the object/scene. Also known as view volume. For square images, under the PyTorch3D convention, `(+1, +1, znear)` is the top left near corner, and `(-1, -1, zfar)` is the bottom right far corner of the volume. For non-square images, the side of the volume in `XY` with the smallest length ranges from `[-1, 1]` while the larger side from `[-s, s]`, where `s` is the aspect ratio and `s > 1` (larger divided by smaller side).
|
This is the normalized coordinate system that confines in a volume the rendered part of the object/scene. Also known as view volume. For square images, under the PyTorch3D convention, `(+1, +1, znear)` is the top left near corner, and `(-1, -1, zfar)` is the bottom right far corner of the volume. For non-square images, the side of the volume in `XY` with the smallest length ranges from `[-1, 1]` while the larger side from `[-s, s]`, where `s` is the aspect ratio and `s > 1` (larger divided by smaller side).
|
||||||
The transformation from view to NDC happens after applying the camera projection matrix (`P`).
|
The transformation from view to NDC happens after applying the camera projection matrix (`P`).
|
||||||
* **Screen coordinate system**
|
* **Screen coordinate system**
|
||||||
This is another representation of the view volume with the `XY` coordinates defined in pixel space instead of a normalized space.
|
This is another representation of the view volume with the `XY` coordinates defined in pixel space instead of a normalized space. (0,0) is the top left corner of the top left pixel
|
||||||
|
and (W,H) is the bottom right corner of the bottom right pixel.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
An illustration of the 4 coordinate systems is shown below
|
An illustration of the 4 coordinate systems is shown below
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Defining Cameras in PyTorch3D
|
## Defining Cameras in PyTorch3D
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -83,8 +84,8 @@ cameras_ndc = PerspectiveCameras(focal_length=fcl_ndc, principal_point=prp_ndc)
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
# Screen space camera
|
# Screen space camera
|
||||||
image_size = ((128, 256),) # (h, w)
|
image_size = ((128, 256),) # (h, w)
|
||||||
fcl_screen = (76.2,) # fcl_ndc * (min(image_size) - 1) / 2
|
fcl_screen = (76.8,) # fcl_ndc * min(image_size) / 2
|
||||||
prp_screen = ((114.8, 31.75), ) # (w - 1) / 2 - px_ndc * (min(image_size) - 1) / 2, (h - 1) / 2 - py_ndc * (min(image_size) - 1) / 2
|
prp_screen = ((115.2, 48), ) # w / 2 - px_ndc * min(image_size) / 2, h / 2 - py_ndc * min(image_size) / 2
|
||||||
cameras_screen = PerspectiveCameras(focal_length=fcl_screen, principal_point=prp_screen, in_ndc=False, image_size=image_size)
|
cameras_screen = PerspectiveCameras(focal_length=fcl_screen, principal_point=prp_screen, in_ndc=False, image_size=image_size)
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -92,9 +93,9 @@ The relationship between screen and NDC specifications of a camera's `focal_leng
|
|||||||
The transformation of x and y coordinates between screen and NDC is exactly the same as for px and py.
|
The transformation of x and y coordinates between screen and NDC is exactly the same as for px and py.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
fx_ndc = fx_screen * 2.0 / (s - 1)
|
fx_ndc = fx_screen * 2.0 / s
|
||||||
fy_ndc = fy_screen * 2.0 / (s - 1)
|
fy_ndc = fy_screen * 2.0 / s
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
px_ndc = - (px_screen - (image_width - 1) / 2.0) * 2.0 / (s - 1)
|
px_ndc = - (px_screen - image_width / 2.0) * 2.0 / s
|
||||||
py_ndc = - (py_screen - (image_height - 1) / 2.0) * 2.0 / (s - 1)
|
py_ndc = - (py_screen - image_height / 2.0) * 2.0 / s
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -33,9 +33,9 @@ def _cameras_from_opencv_projection(
|
|||||||
# has range [-1, 1] and the largest side has range [-u, u], with u > 1.
|
# has range [-1, 1] and the largest side has range [-u, u], with u > 1.
|
||||||
# This convention is consistent with the PyTorch3D renderer, as well as
|
# This convention is consistent with the PyTorch3D renderer, as well as
|
||||||
# the transformation function `get_ndc_to_screen_transform`.
|
# the transformation function `get_ndc_to_screen_transform`.
|
||||||
scale = (image_size_wh.to(R).min(dim=1, keepdim=True)[0] - 1) / 2.0
|
scale = image_size_wh.to(R).min(dim=1, keepdim=True)[0] / 2.0
|
||||||
scale = scale.expand(-1, 2)
|
scale = scale.expand(-1, 2)
|
||||||
c0 = (image_size_wh - 1) / 2.0
|
c0 = image_size_wh / 2.0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Get the PyTorch3D focal length and principal point.
|
# Get the PyTorch3D focal length and principal point.
|
||||||
focal_pytorch3d = focal_length / scale
|
focal_pytorch3d = focal_length / scale
|
||||||
@@ -75,9 +75,9 @@ def _opencv_from_cameras_projection(
|
|||||||
image_size_wh = image_size.to(R).flip(dims=(1,))
|
image_size_wh = image_size.to(R).flip(dims=(1,))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# NDC to screen conversion.
|
# NDC to screen conversion.
|
||||||
scale = (image_size_wh.to(R).min(dim=1, keepdim=True)[0] - 1) / 2.0
|
scale = image_size_wh.to(R).min(dim=1, keepdim=True)[0] / 2.0
|
||||||
scale = scale.expand(-1, 2)
|
scale = scale.expand(-1, 2)
|
||||||
c0 = (image_size_wh - 1) / 2.0
|
c0 = image_size_wh / 2.0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# pyre-fixme[29]: `Union[BoundMethod[typing.Callable(torch.Tensor.__neg__)[[Named...
|
# pyre-fixme[29]: `Union[BoundMethod[typing.Callable(torch.Tensor.__neg__)[[Named...
|
||||||
principal_point = -p0_pytorch3d * scale + c0
|
principal_point = -p0_pytorch3d * scale + c0
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -36,8 +36,9 @@ class CamerasBase(TensorProperties):
|
|||||||
and translation (T)
|
and translation (T)
|
||||||
- NDC coordinate system: This is the normalized coordinate system that confines
|
- NDC coordinate system: This is the normalized coordinate system that confines
|
||||||
in a volume the rendered part of the object or scene. Also known as view volume.
|
in a volume the rendered part of the object or scene. Also known as view volume.
|
||||||
For square images, given the PyTorch3D convention, (+1, +1, znear) is the top left near corner,
|
For square images, given the PyTorch3D convention, (+1, +1, znear)
|
||||||
and (-1, -1, zfar) is the bottom right far corner of the volume.
|
is the top left near corner, and (-1, -1, zfar) is the bottom right far
|
||||||
|
corner of the volume.
|
||||||
The transformation from view --> NDC happens after applying the camera
|
The transformation from view --> NDC happens after applying the camera
|
||||||
projection matrix (P) if defined in NDC space.
|
projection matrix (P) if defined in NDC space.
|
||||||
For non square images, we scale the points such that smallest side
|
For non square images, we scale the points such that smallest side
|
||||||
@@ -1623,12 +1624,12 @@ def get_ndc_to_screen_transform(
|
|||||||
# For non square images, we scale the points such that smallest side
|
# For non square images, we scale the points such that smallest side
|
||||||
# has range [-1, 1] and the largest side has range [-u, u], with u > 1.
|
# has range [-1, 1] and the largest side has range [-u, u], with u > 1.
|
||||||
# This convention is consistent with the PyTorch3D renderer
|
# This convention is consistent with the PyTorch3D renderer
|
||||||
scale = (image_size.min(dim=1).values - 1.0) / 2.0
|
scale = (image_size.min(dim=1).values - 0.0) / 2.0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
K[:, 0, 0] = scale
|
K[:, 0, 0] = scale
|
||||||
K[:, 1, 1] = scale
|
K[:, 1, 1] = scale
|
||||||
K[:, 0, 3] = -1.0 * (width - 1.0) / 2.0
|
K[:, 0, 3] = -1.0 * (width - 0.0) / 2.0
|
||||||
K[:, 1, 3] = -1.0 * (height - 1.0) / 2.0
|
K[:, 1, 3] = -1.0 * (height - 0.0) / 2.0
|
||||||
K[:, 2, 2] = 1.0
|
K[:, 2, 2] = 1.0
|
||||||
K[:, 3, 3] = 1.0
|
K[:, 3, 3] = 1.0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -130,9 +130,9 @@ def ndc_to_screen_points_naive(points, imsize):
|
|||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
height, width = imsize.unbind(1)
|
height, width = imsize.unbind(1)
|
||||||
width = width.view(-1, 1)
|
width = width.view(-1, 1)
|
||||||
half_width = (width - 1.0) / 2.0
|
half_width = width / 2.0
|
||||||
height = height.view(-1, 1)
|
height = height.view(-1, 1)
|
||||||
half_height = (height - 1.0) / 2.0
|
half_height = height / 2.0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
scale = (
|
scale = (
|
||||||
half_width * (height > width).float() + half_height * (height <= width).float()
|
half_width * (height > width).float() + half_height * (height <= width).float()
|
||||||
@@ -524,7 +524,7 @@ class TestCamerasCommon(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
|||||||
# (height, width)
|
# (height, width)
|
||||||
image_size = torch.randint(low=2, high=64, size=(batch_size, 2))
|
image_size = torch.randint(low=2, high=64, size=(batch_size, 2))
|
||||||
# scale
|
# scale
|
||||||
scale = (image_size.min(dim=1, keepdim=True).values - 1.0) / 2.0
|
scale = (image_size.min(dim=1, keepdim=True).values) / 2.0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
ndc_cam_params["focal_length"] = fcl
|
ndc_cam_params["focal_length"] = fcl
|
||||||
ndc_cam_params["principal_point"] = prc
|
ndc_cam_params["principal_point"] = prc
|
||||||
@@ -533,7 +533,7 @@ class TestCamerasCommon(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
|||||||
screen_cam_params["image_size"] = image_size
|
screen_cam_params["image_size"] = image_size
|
||||||
screen_cam_params["focal_length"] = fcl * scale
|
screen_cam_params["focal_length"] = fcl * scale
|
||||||
screen_cam_params["principal_point"] = (
|
screen_cam_params["principal_point"] = (
|
||||||
image_size[:, [1, 0]] - 1.0
|
image_size[:, [1, 0]]
|
||||||
) / 2.0 - prc * scale
|
) / 2.0 - prc * scale
|
||||||
screen_cam_params["in_ndc"] = False
|
screen_cam_params["in_ndc"] = False
|
||||||
else:
|
else:
|
||||||
@@ -821,7 +821,7 @@ class TestFoVPerspectiveProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
|||||||
def test_perspective_type(self):
|
def test_perspective_type(self):
|
||||||
cam = FoVPerspectiveCameras(znear=1.0, zfar=10.0, fov=60.0)
|
cam = FoVPerspectiveCameras(znear=1.0, zfar=10.0, fov=60.0)
|
||||||
self.assertTrue(cam.is_perspective())
|
self.assertTrue(cam.is_perspective())
|
||||||
self.assertEquals(cam.get_znear(), 1.0)
|
self.assertEqual(cam.get_znear(), 1.0)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
############################################################
|
############################################################
|
||||||
@@ -917,7 +917,7 @@ class TestFoVOrthographicProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
|||||||
def test_perspective_type(self):
|
def test_perspective_type(self):
|
||||||
cam = FoVOrthographicCameras(znear=1.0, zfar=10.0)
|
cam = FoVOrthographicCameras(znear=1.0, zfar=10.0)
|
||||||
self.assertFalse(cam.is_perspective())
|
self.assertFalse(cam.is_perspective())
|
||||||
self.assertEquals(cam.get_znear(), 1.0)
|
self.assertEqual(cam.get_znear(), 1.0)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
############################################################
|
############################################################
|
||||||
@@ -974,7 +974,7 @@ class TestOrthographicProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
|||||||
def test_perspective_type(self):
|
def test_perspective_type(self):
|
||||||
cam = OrthographicCameras(focal_length=5.0, principal_point=((2.5, 2.5),))
|
cam = OrthographicCameras(focal_length=5.0, principal_point=((2.5, 2.5),))
|
||||||
self.assertFalse(cam.is_perspective())
|
self.assertFalse(cam.is_perspective())
|
||||||
self.assertEquals(cam.get_znear(), None)
|
self.assertIsNone(cam.get_znear())
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
############################################################
|
############################################################
|
||||||
@@ -1026,4 +1026,4 @@ class TestPerspectiveProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
|||||||
def test_perspective_type(self):
|
def test_perspective_type(self):
|
||||||
cam = PerspectiveCameras(focal_length=5.0, principal_point=((2.5, 2.5),))
|
cam = PerspectiveCameras(focal_length=5.0, principal_point=((2.5, 2.5),))
|
||||||
self.assertTrue(cam.is_perspective())
|
self.assertTrue(cam.is_perspective())
|
||||||
self.assertEquals(cam.get_znear(), None)
|
self.assertIsNone(cam.get_znear())
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -250,23 +250,14 @@ class TestRenderMeshes(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
|||||||
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(
|
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(
|
||||||
image_size=512, blur_radius=0.0, faces_per_pixel=1
|
image_size=512, blur_radius=0.0, faces_per_pixel=1
|
||||||
)
|
)
|
||||||
|
half_half = (512.0 / 2.0, 512.0 / 2.0)
|
||||||
for cam_type in (PerspectiveCameras, OrthographicCameras):
|
for cam_type in (PerspectiveCameras, OrthographicCameras):
|
||||||
cameras = cam_type(
|
cameras = cam_type(
|
||||||
device=device,
|
device=device,
|
||||||
R=R,
|
R=R,
|
||||||
T=T,
|
T=T,
|
||||||
principal_point=(
|
principal_point=(half_half,),
|
||||||
(
|
focal_length=(half_half,),
|
||||||
(512.0 - 1.0) / 2.0,
|
|
||||||
(512.0 - 1.0) / 2.0,
|
|
||||||
),
|
|
||||||
),
|
|
||||||
focal_length=(
|
|
||||||
(
|
|
||||||
(512.0 - 1.0) / 2.0,
|
|
||||||
(512.0 - 1.0) / 2.0,
|
|
||||||
),
|
|
||||||
),
|
|
||||||
image_size=((512, 512),),
|
image_size=((512, 512),),
|
||||||
in_ndc=False,
|
in_ndc=False,
|
||||||
)
|
)
|
||||||
@@ -285,6 +276,10 @@ class TestRenderMeshes(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
|||||||
images = renderer(sphere_mesh)
|
images = renderer(sphere_mesh)
|
||||||
rgb = images[0, ..., :3].squeeze().cpu()
|
rgb = images[0, ..., :3].squeeze().cpu()
|
||||||
filename = "test_simple_sphere_light_phong_%s.png" % cam_type.__name__
|
filename = "test_simple_sphere_light_phong_%s.png" % cam_type.__name__
|
||||||
|
if DEBUG:
|
||||||
|
Image.fromarray((rgb.numpy() * 255).astype(np.uint8)).save(
|
||||||
|
DATA_DIR / f"{filename}_.png"
|
||||||
|
)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
image_ref = load_rgb_image(filename, DATA_DIR)
|
image_ref = load_rgb_image(filename, DATA_DIR)
|
||||||
self.assertClose(rgb, image_ref, atol=0.05)
|
self.assertClose(rgb, image_ref, atol=0.05)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user