camera refactoring
Summary: Refactor cameras * CamerasBase was enhanced with `transform_points_screen` that transforms projected points from NDC to screen space * OpenGLPerspective, OpenGLOrthographic -> FoVPerspective, FoVOrthographic * SfMPerspective, SfMOrthographic -> Perspective, Orthographic * PerspectiveCamera can optionally be constructred with screen space parameters * Note on Cameras and coordinate systems was added Reviewed By: nikhilaravi Differential Revision: D23168525 fbshipit-source-id: dd138e2b2cc7e0e0d9f34c45b8251c01266a2063
63
docs/notes/cameras.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
# Cameras
|
||||
|
||||
## Camera Coordinate Systems
|
||||
|
||||
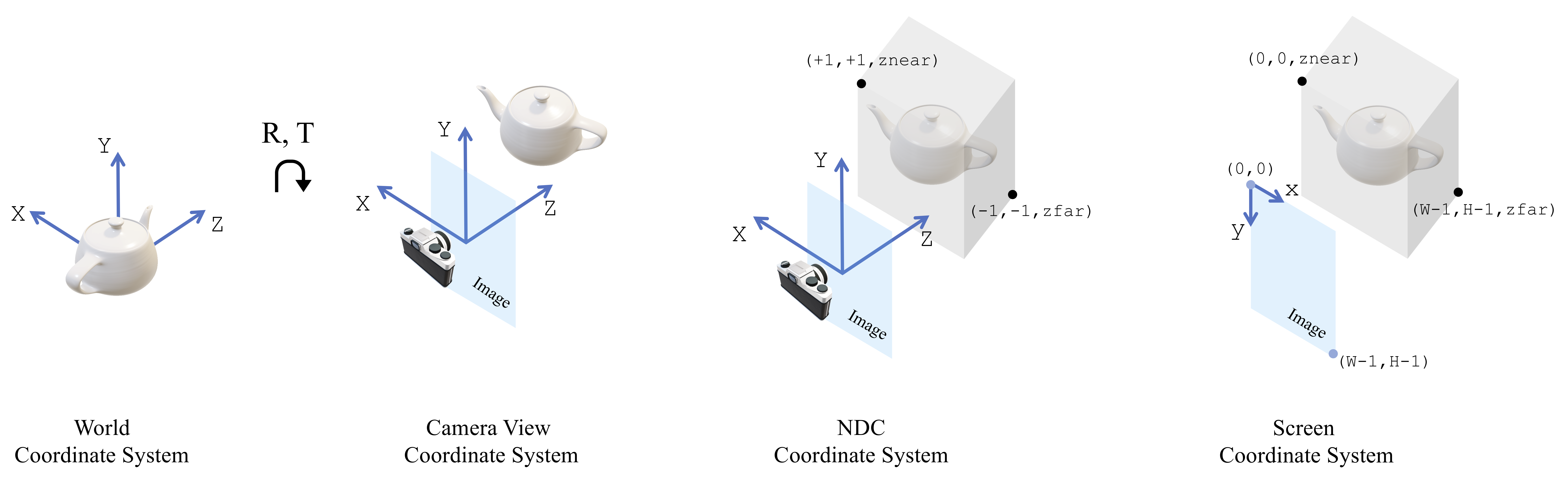
When working with 3D data, there are 4 coordinate systems users need to know
|
||||
* **World coordinate system**
|
||||
This is the system the object/scene lives - the world.
|
||||
* **Camera view coordinate system**
|
||||
This is the system that has its origin on the image plane and the `Z`-axis perpendicular to the image plane. In PyTorch3D, we assume that `+X` points left, and `+Y` points up and `+Z` points out from the image plane. The transformation from world to view happens after applying a rotation (`R`) and translation (`T`).
|
||||
* **NDC coordinate system**
|
||||
This is the normalized coordinate system that confines in a volume the renderered part of the object/scene. Also known as view volume. Under the PyTorch3D convention, `(+1, +1, znear)` is the top left near corner, and `(-1, -1, zfar)` is the bottom right far corner of the volume. The transformation from view to NDC happens after applying the camera projection matrix (`P`).
|
||||
* **Screen coordinate system**
|
||||
This is another representation of the view volume with the `XY` coordinates defined in pixel space instead of a normalized space.
|
||||
|
||||
An illustration of the 4 coordinate systems is shown below
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Defining Cameras in PyTorch3D
|
||||
|
||||
Cameras in PyTorch3D transform an object/scene from world to NDC by first transforming the object/scene to view (via transforms `R` and `T`) and then projecting the 3D object/scene to NDC (via the projection matrix `P`, else known as camera matrix). Thus, the camera parameters in `P` are assumed to be in NDC space. If the user has camera parameters in screen space, which is a common use case, the parameters should transformed to NDC (see below for an example)
|
||||
|
||||
We describe the camera types in PyTorch3D and the convention for the camera parameters provided at construction time.
|
||||
|
||||
### Camera Types
|
||||
|
||||
All cameras inherit from `CamerasBase` which is a base class for all cameras. PyTorch3D provides four different camera types. The `CamerasBase` defines methods that are common to all camera models:
|
||||
* `get_camera_center` that returns the optical center of the camera in world coordinates
|
||||
* `get_world_to_view_transform` which returns a 3D transform from world coordinates to the camera view coordinates (R, T)
|
||||
* `get_full_projection_transform` which composes the projection transform (P) with the world-to-view transform (R, T)
|
||||
* `transform_points` which takes a set of input points in world coordinates and projects to NDC coordinates ranging from [-1, -1, znear] to [+1, +1, zfar].
|
||||
* `transform_points_screen` which takes a set of input points in world coordinates and projects them to the screen coordinates ranging from [0, 0, znear] to [W-1, H-1, zfar]
|
||||
|
||||
Users can easily customize their own cameras. For each new camera, users should implement the `get_projection_transform` routine that returns the mapping `P` from camera view coordinates to NDC coordinates.
|
||||
|
||||
#### FoVPerspectiveCameras, FoVOrthographicCameras
|
||||
These two cameras follow the OpenGL convention for perspective and orthographic cameras respectively. The user provides the near `znear` and far `zfar` field which confines the view volume in the `Z` axis. The view volume in the `XY` plane is defined by field of view angle (`fov`) in the case of `FoVPerspectiveCameras` and by `min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y` in the case of `FoVOrthographicCameras`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### PerspectiveCameras, OrthographicCameras
|
||||
These two cameras follow the Multi-View Geometry convention for cameras. The user provides the focal length (`fx`, `fy`) and the principal point (`px`, `py`). For example, `camera = PerspectiveCameras(focal_length=((fx, fy),), principal_point=((px, py),))`
|
||||
|
||||
As mentioned above, the focal length and principal point are used to convert a point `(X, Y, Z)` from view coordinates to NDC coordinates, as follows
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# for perspective
|
||||
x_ndc = fx * X / Z + px
|
||||
y_ndc = fy * Y / Z + py
|
||||
z_ndc = 1 / Z
|
||||
|
||||
# for orthographic
|
||||
x_ndc = fx * X + px
|
||||
y_ndc = fy * Y + py
|
||||
z_ndc = Z
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Commonly, users have access to the focal length (`fx_screen`, `fy_screen`) and the principal point (`px_screen`, `py_screen`) in screen space. In that case, to construct the camera the user needs to additionally provide the `image_size = ((image_width, image_height),)`. More precisely, `camera = PerspectiveCameras(focal_length=((fx_screen, fy_screen),), principal_point=((px_screen, py_screen),), image_size = ((image_width, image_height),))`. Internally, the camera parameters are converted from screen to NDC as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
fx = fx_screen * 2.0 / image_width
|
||||
fy = fy_screen * 2.0 / image_height
|
||||
|
||||
px = - (px_screen - image_width / 2.0) * 2.0 / image_width
|
||||
py = - (py_screen - image_height / 2.0) * 2.0/ image_height
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ Rendering requires transformations between several different coordinate frames:
|
||||
<img src="assets/transformations_overview.png" width="1000">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For example, given a teapot mesh, the world coordinate frame, camera coordiante frame and image are show in the figure below. Note that the world and camera coordinate frames have the +z direction pointing in to the page.
|
||||
For example, given a teapot mesh, the world coordinate frame, camera coordiante frame and image are show in the figure below. Note that the world and camera coordinate frames have the +z direction pointing in to the page.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="assets/world_camera_image.png" width="1000">
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -47,8 +47,8 @@ For example, given a teapot mesh, the world coordinate frame, camera coordiante
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE: PyTorch3D vs OpenGL**
|
||||
|
||||
While we tried to emulate several aspects of OpenGL, there are differences in the coordinate frame conventions.
|
||||
- The default world coordinate frame in PyTorch3D has +Z pointing in to the screen whereas in OpenGL, +Z is pointing out of the screen. Both are right handed.
|
||||
While we tried to emulate several aspects of OpenGL, there are differences in the coordinate frame conventions.
|
||||
- The default world coordinate frame in PyTorch3D has +Z pointing in to the screen whereas in OpenGL, +Z is pointing out of the screen. Both are right handed.
|
||||
- The NDC coordinate system in PyTorch3D is **right-handed** compared with a **left-handed** NDC coordinate system in OpenGL (the projection matrix switches the handedness).
|
||||
|
||||
<img align="center" src="assets/opengl_coordframes.png" width="300">
|
||||
@@ -61,14 +61,14 @@ A renderer in PyTorch3D is composed of a **rasterizer** and a **shader**. Create
|
||||
```
|
||||
# Imports
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer import (
|
||||
OpenGLPerspectiveCameras, look_at_view_transform,
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras, look_at_view_transform,
|
||||
RasterizationSettings, BlendParams,
|
||||
MeshRenderer, MeshRasterizer, HardPhongShader
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize an OpenGL perspective camera.
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(2.7, 10, 20)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
|
||||
# Define the settings for rasterization and shading. Here we set the output image to be of size
|
||||
# 512x512. As we are rendering images for visualization purposes only we will set faces_per_pixel=1
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -102,7 +102,7 @@
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# rendering components\n",
|
||||
"from pytorch3d.renderer import (\n",
|
||||
" OpenGLPerspectiveCameras, look_at_view_transform, look_at_rotation, \n",
|
||||
" FoVPerspectiveCameras, look_at_view_transform, look_at_rotation, \n",
|
||||
" RasterizationSettings, MeshRenderer, MeshRasterizer, BlendParams,\n",
|
||||
" SoftSilhouetteShader, HardPhongShader, PointLights\n",
|
||||
")"
|
||||
@@ -217,8 +217,8 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Initialize an OpenGL perspective camera.\n",
|
||||
"cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device)\n",
|
||||
"# Initialize a perspective camera.\n",
|
||||
"cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# To blend the 100 faces we set a few parameters which control the opacity and the sharpness of \n",
|
||||
"# edges. Refer to blending.py for more details. \n",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -129,7 +129,7 @@
|
||||
"from pytorch3d.structures import Meshes, Textures\n",
|
||||
"from pytorch3d.renderer import (\n",
|
||||
" look_at_view_transform,\n",
|
||||
" OpenGLPerspectiveCameras, \n",
|
||||
" FoVPerspectiveCameras, \n",
|
||||
" PointLights, \n",
|
||||
" DirectionalLights, \n",
|
||||
" Materials, \n",
|
||||
@@ -309,16 +309,16 @@
|
||||
"# the cow is facing the -z direction. \n",
|
||||
"lights = PointLights(device=device, location=[[0.0, 0.0, -3.0]])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Initialize an OpenGL perspective camera that represents a batch of different \n",
|
||||
"# Initialize a camera that represents a batch of different \n",
|
||||
"# viewing angles. All the cameras helper methods support mixed type inputs and \n",
|
||||
"# broadcasting. So we can view the camera from the a distance of dist=2.7, and \n",
|
||||
"# then specify elevation and azimuth angles for each viewpoint as tensors. \n",
|
||||
"R, T = look_at_view_transform(dist=2.7, elev=elev, azim=azim)\n",
|
||||
"cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)\n",
|
||||
"cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# We arbitrarily choose one particular view that will be used to visualize \n",
|
||||
"# results\n",
|
||||
"camera = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R[None, 1, ...], \n",
|
||||
"camera = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R[None, 1, ...], \n",
|
||||
" T=T[None, 1, ...]) \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Define the settings for rasterization and shading. Here we set the output \n",
|
||||
@@ -361,7 +361,7 @@
|
||||
"# Our multi-view cow dataset will be represented by these 2 lists of tensors,\n",
|
||||
"# each of length num_views.\n",
|
||||
"target_rgb = [target_images[i, ..., :3] for i in range(num_views)]\n",
|
||||
"target_cameras = [OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R[None, i, ...], \n",
|
||||
"target_cameras = [FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R[None, i, ...], \n",
|
||||
" T=T[None, i, ...]) for i in range(num_views)]"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
@@ -925,4 +925,4 @@
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -64,7 +64,7 @@
|
||||
"from pytorch3d.structures import Pointclouds\n",
|
||||
"from pytorch3d.renderer import (\n",
|
||||
" look_at_view_transform,\n",
|
||||
" OpenGLOrthographicCameras, \n",
|
||||
" FoVOrthographicCameras, \n",
|
||||
" PointsRasterizationSettings,\n",
|
||||
" PointsRenderer,\n",
|
||||
" PointsRasterizer,\n",
|
||||
@@ -147,9 +147,9 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Initialize an OpenGL perspective camera.\n",
|
||||
"# Initialize a camera.\n",
|
||||
"R, T = look_at_view_transform(20, 10, 0)\n",
|
||||
"cameras = OpenGLOrthographicCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T, znear=0.01)\n",
|
||||
"cameras = FoVOrthographicCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T, znear=0.01)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Define the settings for rasterization and shading. Here we set the output image to be of size\n",
|
||||
"# 512x512. As we are rendering images for visualization purposes only we will set faces_per_pixel=1\n",
|
||||
@@ -195,9 +195,9 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Initialize an OpenGL perspective camera.\n",
|
||||
"# Initialize a camera.\n",
|
||||
"R, T = look_at_view_transform(20, 10, 0)\n",
|
||||
"cameras = OpenGLOrthographicCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T, znear=0.01)\n",
|
||||
"cameras = FoVOrthographicCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T, znear=0.01)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Define the settings for rasterization and shading. Here we set the output image to be of size\n",
|
||||
"# 512x512. As we are rendering images for visualization purposes only we will set faces_per_pixel=1\n",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -90,7 +90,7 @@
|
||||
"from pytorch3d.structures import Meshes, Textures\n",
|
||||
"from pytorch3d.renderer import (\n",
|
||||
" look_at_view_transform,\n",
|
||||
" OpenGLPerspectiveCameras, \n",
|
||||
" FoVPerspectiveCameras, \n",
|
||||
" PointLights, \n",
|
||||
" DirectionalLights, \n",
|
||||
" Materials, \n",
|
||||
@@ -286,11 +286,11 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Initialize an OpenGL perspective camera.\n",
|
||||
"# Initialize a camera.\n",
|
||||
"# With world coordinates +Y up, +X left and +Z in, the front of the cow is facing the -Z direction. \n",
|
||||
"# So we move the camera by 180 in the azimuth direction so it is facing the front of the cow. \n",
|
||||
"R, T = look_at_view_transform(2.7, 0, 180) \n",
|
||||
"cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)\n",
|
||||
"cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Define the settings for rasterization and shading. Here we set the output image to be of size\n",
|
||||
"# 512x512. As we are rendering images for visualization purposes only we will set faces_per_pixel=1\n",
|
||||
@@ -444,7 +444,7 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Rotate the object by increasing the elevation and azimuth angles\n",
|
||||
"R, T = look_at_view_transform(dist=2.7, elev=10, azim=-150)\n",
|
||||
"cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)\n",
|
||||
"cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Move the light location so the light is shining on the cow's face. \n",
|
||||
"lights.location = torch.tensor([[2.0, 2.0, -2.0]], device=device)\n",
|
||||
@@ -519,7 +519,7 @@
|
||||
"# view the camera from the same distance and specify dist=2.7 as a float,\n",
|
||||
"# and then specify elevation and azimuth angles for each viewpoint as tensors. \n",
|
||||
"R, T = look_at_view_transform(dist=2.7, elev=elev, azim=azim)\n",
|
||||
"cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)\n",
|
||||
"cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Move the light back in front of the cow which is facing the -z direction.\n",
|
||||
"lights.location = torch.tensor([[0.0, 0.0, -3.0]], device=device)"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ from pytorch3d.renderer import (
|
||||
HardPhongShader,
|
||||
MeshRasterizer,
|
||||
MeshRenderer,
|
||||
OpenGLPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
PointLights,
|
||||
RasterizationSettings,
|
||||
TexturesVertex,
|
||||
@@ -125,7 +125,7 @@ class ShapeNetBase(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
|
||||
meshes.textures = TexturesVertex(
|
||||
verts_features=torch.ones_like(meshes.verts_padded(), device=device)
|
||||
)
|
||||
cameras = kwargs.get("cameras", OpenGLPerspectiveCameras()).to(device)
|
||||
cameras = kwargs.get("cameras", FoVPerspectiveCameras()).to(device)
|
||||
if len(cameras) != 1 and len(cameras) % len(meshes) != 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Mismatch between batch dims of cameras and meshes.")
|
||||
if len(cameras) > 1:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,11 +6,15 @@ from .blending import (
|
||||
sigmoid_alpha_blend,
|
||||
softmax_rgb_blend,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .cameras import OpenGLOrthographicCameras # deprecated
|
||||
from .cameras import OpenGLPerspectiveCameras # deprecated
|
||||
from .cameras import SfMOrthographicCameras # deprecated
|
||||
from .cameras import SfMPerspectiveCameras # deprecated
|
||||
from .cameras import (
|
||||
OpenGLOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
OpenGLPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
SfMOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
SfMPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
FoVOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
OrthographicCameras,
|
||||
PerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
camera_position_from_spherical_angles,
|
||||
get_world_to_view_transform,
|
||||
look_at_rotation,
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
# Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
import math
|
||||
import warnings
|
||||
from typing import Optional, Sequence, Tuple
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
@@ -20,23 +21,43 @@ class CamerasBase(TensorProperties):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
`CamerasBase` implements a base class for all cameras.
|
||||
|
||||
For cameras, there are four different coordinate systems (or spaces)
|
||||
- World coordinate system: This is the system the object lives - the world.
|
||||
- Camera view coordinate system: This is the system that has its origin on the image plane
|
||||
and the and the Z-axis perpendicular to the image plane.
|
||||
In PyTorch3D, we assume that +X points left, and +Y points up and
|
||||
+Z points out from the image plane.
|
||||
The transformation from world -> view happens after applying a rotation (R)
|
||||
and translation (T)
|
||||
- NDC coordinate system: This is the normalized coordinate system that confines
|
||||
in a volume the renderered part of the object or scene. Also known as view volume.
|
||||
Given the PyTorch3D convention, (+1, +1, znear) is the top left near corner,
|
||||
and (-1, -1, zfar) is the bottom right far corner of the volume.
|
||||
The transformation from view -> NDC happens after applying the camera
|
||||
projection matrix (P).
|
||||
- Screen coordinate system: This is another representation of the view volume with
|
||||
the XY coordinates defined in pixel space instead of a normalized space.
|
||||
|
||||
A better illustration of the coordinate systems can be found in pytorch3d/docs/notes/cameras.md.
|
||||
|
||||
It defines methods that are common to all camera models:
|
||||
- `get_camera_center` that returns the optical center of the camera in
|
||||
world coordinates
|
||||
- `get_world_to_view_transform` which returns a 3D transform from
|
||||
world coordinates to the camera coordinates
|
||||
world coordinates to the camera view coordinates (R, T)
|
||||
- `get_full_projection_transform` which composes the projection
|
||||
transform with the world-to-view transform
|
||||
- `transform_points` which takes a set of input points and
|
||||
projects them onto a 2D camera plane.
|
||||
transform (P) with the world-to-view transform (R, T)
|
||||
- `transform_points` which takes a set of input points in world coordinates and
|
||||
projects to NDC coordinates ranging from [-1, -1, znear] to [+1, +1, zfar].
|
||||
- `transform_points_screen` which takes a set of input points in world coordinates and
|
||||
projects them to the screen coordinates ranging from [0, 0, znear] to [W-1, H-1, zfar]
|
||||
|
||||
For each new camera, one should implement the `get_projection_transform`
|
||||
routine that returns the mapping from camera coordinates in world units
|
||||
to the screen coordinates.
|
||||
routine that returns the mapping from camera view coordinates to NDC coordinates.
|
||||
|
||||
Another useful function that is specific to each camera model is
|
||||
`unproject_points` which sends points from screen coordinates back to
|
||||
camera or world coordinates depending on the `world_coordinates`
|
||||
`unproject_points` which sends points from NDC coordinates back to
|
||||
camera view or world coordinates depending on the `world_coordinates`
|
||||
boolean argument of the function.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -56,7 +77,7 @@ class CamerasBase(TensorProperties):
|
||||
|
||||
def unproject_points(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Transform input points in screen coodinates
|
||||
Transform input points from NDC coodinates
|
||||
to the world / camera coordinates.
|
||||
|
||||
Each of the input points `xy_depth` of shape (..., 3) is
|
||||
@@ -74,7 +95,7 @@ class CamerasBase(TensorProperties):
|
||||
|
||||
cameras = # camera object derived from CamerasBase
|
||||
xyz = # 3D points of shape (batch_size, num_points, 3)
|
||||
# transform xyz to the camera coordinates
|
||||
# transform xyz to the camera view coordinates
|
||||
xyz_cam = cameras.get_world_to_view_transform().transform_points(xyz)
|
||||
# extract the depth of each point as the 3rd coord of xyz_cam
|
||||
depth = xyz_cam[:, :, 2:]
|
||||
@@ -94,7 +115,7 @@ class CamerasBase(TensorProperties):
|
||||
world_coordinates: If `True`, unprojects the points back to world
|
||||
coordinates using the camera extrinsics `R` and `T`.
|
||||
`False` ignores `R` and `T` and unprojects to
|
||||
the camera coordinates.
|
||||
the camera view coordinates.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
new_points: unprojected points with the same shape as `xy_depth`.
|
||||
@@ -141,7 +162,7 @@ class CamerasBase(TensorProperties):
|
||||
lighting calculations.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
T: a Transform3d object which represents a batch of transforms
|
||||
A Transform3d object which represents a batch of transforms
|
||||
of shape (N, 3, 3)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.R = kwargs.get("R", self.R) # pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
@@ -151,8 +172,8 @@ class CamerasBase(TensorProperties):
|
||||
|
||||
def get_full_projection_transform(self, **kwargs) -> Transform3d:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Return the full world-to-screen transform composing the
|
||||
world-to-view and view-to-screen transforms.
|
||||
Return the full world-to-NDC transform composing the
|
||||
world-to-view and view-to-NDC transforms.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
**kwargs: parameters for the projection transforms can be passed in
|
||||
@@ -164,26 +185,26 @@ class CamerasBase(TensorProperties):
|
||||
lighting calculations.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
T: a Transform3d object which represents a batch of transforms
|
||||
a Transform3d object which represents a batch of transforms
|
||||
of shape (N, 3, 3)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.R = kwargs.get("R", self.R) # pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
self.T = kwargs.get("T", self.T) # pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
world_to_view_transform = self.get_world_to_view_transform(R=self.R, T=self.T)
|
||||
view_to_screen_transform = self.get_projection_transform(**kwargs)
|
||||
return world_to_view_transform.compose(view_to_screen_transform)
|
||||
view_to_ndc_transform = self.get_projection_transform(**kwargs)
|
||||
return world_to_view_transform.compose(view_to_ndc_transform)
|
||||
|
||||
def transform_points(
|
||||
self, points, eps: Optional[float] = None, **kwargs
|
||||
) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Transform input points from world to screen space.
|
||||
Transform input points from world to NDC space.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
points: torch tensor of shape (..., 3).
|
||||
eps: If eps!=None, the argument is used to clamp the
|
||||
divisor in the homogeneous normalization of the points
|
||||
transformed to the screen space. Plese see
|
||||
transformed to the ndc space. Please see
|
||||
`transforms.Transform3D.transform_points` for details.
|
||||
|
||||
For `CamerasBase.transform_points`, setting `eps > 0`
|
||||
@@ -194,8 +215,50 @@ class CamerasBase(TensorProperties):
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
new_points: transformed points with the same shape as the input.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
world_to_screen_transform = self.get_full_projection_transform(**kwargs)
|
||||
return world_to_screen_transform.transform_points(points, eps=eps)
|
||||
world_to_ndc_transform = self.get_full_projection_transform(**kwargs)
|
||||
return world_to_ndc_transform.transform_points(points, eps=eps)
|
||||
|
||||
def transform_points_screen(
|
||||
self, points, image_size, eps: Optional[float] = None, **kwargs
|
||||
) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Transform input points from world to screen space.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
points: torch tensor of shape (N, V, 3).
|
||||
image_size: torch tensor of shape (N, 2)
|
||||
eps: If eps!=None, the argument is used to clamp the
|
||||
divisor in the homogeneous normalization of the points
|
||||
transformed to the ndc space. Please see
|
||||
`transforms.Transform3D.transform_points` for details.
|
||||
|
||||
For `CamerasBase.transform_points`, setting `eps > 0`
|
||||
stabilizes gradients since it leads to avoiding division
|
||||
by excessivelly low numbers for points close to the
|
||||
camera plane.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
new_points: transformed points with the same shape as the input.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
ndc_points = self.transform_points(points, eps=eps, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
if not torch.is_tensor(image_size):
|
||||
image_size = torch.tensor(
|
||||
image_size, dtype=torch.int64, device=points.device
|
||||
)
|
||||
if (image_size < 1).any():
|
||||
raise ValueError("Provided image size is invalid.")
|
||||
|
||||
image_width, image_height = image_size.unbind(1)
|
||||
image_width = image_width.view(-1, 1) # (N, 1)
|
||||
image_height = image_height.view(-1, 1) # (N, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
ndc_z = ndc_points[..., 2]
|
||||
screen_x = (image_width - 1.0) / 2.0 * (1.0 - ndc_points[..., 0])
|
||||
screen_y = (image_height - 1.0) / 2.0 * (1.0 - ndc_points[..., 1])
|
||||
|
||||
return torch.stack((screen_x, screen_y, ndc_z), dim=2)
|
||||
|
||||
def clone(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@@ -206,21 +269,56 @@ class CamerasBase(TensorProperties):
|
||||
return super().clone(other)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
########################
|
||||
# Specific camera classes
|
||||
########################
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Field of View Camera Classes #
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
def OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(
|
||||
znear=1.0,
|
||||
zfar=100.0,
|
||||
aspect_ratio=1.0,
|
||||
fov=60.0,
|
||||
degrees: bool = True,
|
||||
R=r,
|
||||
T=t,
|
||||
device="cpu",
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
OpenGLPerspectiveCameras has been DEPRECATED. Use FoVPerspectiveCameras instead.
|
||||
Preserving OpenGLPerspectiveCameras for backward compatibility.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
warnings.warn(
|
||||
"""OpenGLPerspectiveCameras is deprecated,
|
||||
Use FoVPerspectiveCameras instead.
|
||||
OpenGLPerspectiveCameras will be removed in future releases.""",
|
||||
PendingDeprecationWarning,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return FoVPerspectiveCameras(
|
||||
znear=znear,
|
||||
zfar=zfar,
|
||||
aspect_ratio=aspect_ratio,
|
||||
fov=fov,
|
||||
degrees=degrees,
|
||||
R=R,
|
||||
T=T,
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FoVPerspectiveCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A class which stores a batch of parameters to generate a batch of
|
||||
projection matrices using the OpenGL convention for a perspective camera.
|
||||
projection matrices by specifiying the field of view.
|
||||
The definition of the parameters follow the OpenGL perspective camera.
|
||||
|
||||
The extrinsics of the camera (R and T matrices) can also be set in the
|
||||
initializer or passed in to `get_full_projection_transform` to get
|
||||
the full transformation from world -> screen.
|
||||
the full transformation from world -> ndc.
|
||||
|
||||
The `transform_points` method calculates the full world -> screen transform
|
||||
The `transform_points` method calculates the full world -> ndc transform
|
||||
and then applies it to the input points.
|
||||
|
||||
The transforms can also be returned separately as Transform3d objects.
|
||||
@@ -267,8 +365,11 @@ class OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
|
||||
def get_projection_transform(self, **kwargs) -> Transform3d:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Calculate the OpenGL perpective projection matrix with a symmetric
|
||||
Calculate the perpective projection matrix with a symmetric
|
||||
viewing frustrum. Use column major order.
|
||||
The viewing frustrum will be projected into ndc, s.t.
|
||||
(max_x, max_y) -> (+1, +1)
|
||||
(min_x, min_y) -> (-1, -1)
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
**kwargs: parameters for the projection can be passed in as keyword
|
||||
@@ -276,14 +377,14 @@ class OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
|
||||
Return:
|
||||
P: a Transform3d object which represents a batch of projection
|
||||
matrices of shape (N, 3, 3)
|
||||
matrices of shape (N, 4, 4)
|
||||
|
||||
.. code-block:: python
|
||||
|
||||
f1 = -(far + near)/(far−near)
|
||||
f2 = -2*far*near/(far-near)
|
||||
h1 = (top + bottom)/(top - bottom)
|
||||
w1 = (right + left)/(right - left)
|
||||
h1 = (max_y + min_y)/(max_y - min_y)
|
||||
w1 = (max_x + min_x)/(max_x - min_x)
|
||||
tanhalffov = tan((fov/2))
|
||||
s1 = 1/tanhalffov
|
||||
s2 = 1/(tanhalffov * (aspect_ratio))
|
||||
@@ -310,10 +411,10 @@ class OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
if not torch.is_tensor(fov):
|
||||
fov = torch.tensor(fov, device=self.device)
|
||||
tanHalfFov = torch.tan((fov / 2))
|
||||
top = tanHalfFov * znear
|
||||
bottom = -top
|
||||
right = top * aspect_ratio
|
||||
left = -right
|
||||
max_y = tanHalfFov * znear
|
||||
min_y = -max_y
|
||||
max_x = max_y * aspect_ratio
|
||||
min_x = -max_x
|
||||
|
||||
# NOTE: In OpenGL the projection matrix changes the handedness of the
|
||||
# coordinate frame. i.e the NDC space postive z direction is the
|
||||
@@ -323,28 +424,19 @@ class OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
# so the so the z sign is 1.0.
|
||||
z_sign = 1.0
|
||||
|
||||
P[:, 0, 0] = 2.0 * znear / (right - left)
|
||||
P[:, 1, 1] = 2.0 * znear / (top - bottom)
|
||||
P[:, 0, 2] = (right + left) / (right - left)
|
||||
P[:, 1, 2] = (top + bottom) / (top - bottom)
|
||||
P[:, 0, 0] = 2.0 * znear / (max_x - min_x)
|
||||
P[:, 1, 1] = 2.0 * znear / (max_y - min_y)
|
||||
P[:, 0, 2] = (max_x + min_x) / (max_x - min_x)
|
||||
P[:, 1, 2] = (max_y + min_y) / (max_y - min_y)
|
||||
P[:, 3, 2] = z_sign * ones
|
||||
|
||||
# NOTE: This part of the matrix is for z renormalization in OpenGL
|
||||
# which maps the z to [-1, 1]. This won't work yet as the torch3d
|
||||
# rasterizer ignores faces which have z < 0.
|
||||
# P[:, 2, 2] = z_sign * (far + near) / (far - near)
|
||||
# P[:, 2, 3] = -2.0 * far * near / (far - near)
|
||||
# P[:, 3, 2] = z_sign * torch.ones((N))
|
||||
|
||||
# NOTE: This maps the z coordinate from [0, 1] where z = 0 if the point
|
||||
# is at the near clipping plane and z = 1 when the point is at the far
|
||||
# clipping plane. This replaces the OpenGL z normalization to [-1, 1]
|
||||
# until rasterization is changed to clip at z = -1.
|
||||
# clipping plane.
|
||||
P[:, 2, 2] = z_sign * zfar / (zfar - znear)
|
||||
P[:, 2, 3] = -(zfar * znear) / (zfar - znear)
|
||||
|
||||
# OpenGL uses column vectors so need to transpose the projection matrix
|
||||
# as torch3d uses row vectors.
|
||||
# Transpose the projection matrix as PyTorch3d transforms use row vectors.
|
||||
transform = Transform3d(device=self.device)
|
||||
transform._matrix = P.transpose(1, 2).contiguous()
|
||||
return transform
|
||||
@@ -357,7 +449,7 @@ class OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
**kwargs
|
||||
) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
""">!
|
||||
OpenGL cameras further allow for passing depth in world units
|
||||
FoV cameras further allow for passing depth in world units
|
||||
(`scaled_depth_input=False`) or in the [0, 1]-normalized units
|
||||
(`scaled_depth_input=True`)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -367,11 +459,11 @@ class OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
the world units.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# obtain the relevant transformation to screen
|
||||
# obtain the relevant transformation to ndc
|
||||
if world_coordinates:
|
||||
to_screen_transform = self.get_full_projection_transform()
|
||||
to_ndc_transform = self.get_full_projection_transform()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
to_screen_transform = self.get_projection_transform()
|
||||
to_ndc_transform = self.get_projection_transform()
|
||||
|
||||
if scaled_depth_input:
|
||||
# the input is scaled depth, so we don't have to do anything
|
||||
@@ -390,45 +482,84 @@ class OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
xy_sdepth = torch.cat((xy_depth[..., 0:2], sdepth), dim=-1)
|
||||
|
||||
# unproject with inverse of the projection
|
||||
unprojection_transform = to_screen_transform.inverse()
|
||||
unprojection_transform = to_ndc_transform.inverse()
|
||||
return unprojection_transform.transform_points(xy_sdepth)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class OpenGLOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
def OpenGLOrthographicCameras(
|
||||
znear=1.0,
|
||||
zfar=100.0,
|
||||
top=1.0,
|
||||
bottom=-1.0,
|
||||
left=-1.0,
|
||||
right=1.0,
|
||||
scale_xyz=((1.0, 1.0, 1.0),), # (1, 3)
|
||||
R=r,
|
||||
T=t,
|
||||
device="cpu",
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
OpenGLOrthographicCameras has been DEPRECATED. Use FoVOrthographicCameras instead.
|
||||
Preserving OpenGLOrthographicCameras for backward compatibility.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
warnings.warn(
|
||||
"""OpenGLOrthographicCameras is deprecated,
|
||||
Use FoVOrthographicCameras instead.
|
||||
OpenGLOrthographicCameras will be removed in future releases.""",
|
||||
PendingDeprecationWarning,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return FoVOrthographicCameras(
|
||||
znear=znear,
|
||||
zfar=zfar,
|
||||
max_y=top,
|
||||
min_y=bottom,
|
||||
max_x=right,
|
||||
min_x=left,
|
||||
scale_xyz=scale_xyz,
|
||||
R=R,
|
||||
T=T,
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FoVOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A class which stores a batch of parameters to generate a batch of
|
||||
transformation matrices using the OpenGL convention for orthographic camera.
|
||||
projection matrices by specifiying the field of view.
|
||||
The definition of the parameters follow the OpenGL orthographic camera.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
znear=1.0,
|
||||
zfar=100.0,
|
||||
top=1.0,
|
||||
bottom=-1.0,
|
||||
left=-1.0,
|
||||
right=1.0,
|
||||
max_y=1.0,
|
||||
min_y=-1.0,
|
||||
max_x=1.0,
|
||||
min_x=-1.0,
|
||||
scale_xyz=((1.0, 1.0, 1.0),), # (1, 3)
|
||||
R=r,
|
||||
T=t,
|
||||
device="cpu",
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
__init__(self, znear, zfar, top, bottom, left, right, scale_xyz, R, T, device) -> None # noqa
|
||||
__init__(self, znear, zfar, max_y, min_y, max_x, min_x, scale_xyz, R, T, device) -> None # noqa
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
znear: near clipping plane of the view frustrum.
|
||||
zfar: far clipping plane of the view frustrum.
|
||||
top: position of the top of the screen.
|
||||
bottom: position of the bottom of the screen.
|
||||
left: position of the left of the screen.
|
||||
right: position of the right of the screen.
|
||||
max_y: maximum y coordinate of the frustrum.
|
||||
min_y: minimum y coordinate of the frustrum.
|
||||
max_x: maximum x coordinate of the frustrum.
|
||||
min_x: minumum x coordinage of the frustrum
|
||||
scale_xyz: scale factors for each axis of shape (N, 3).
|
||||
R: Rotation matrix of shape (N, 3, 3).
|
||||
T: Translation of shape (N, 3).
|
||||
device: torch.device or string.
|
||||
|
||||
Only need to set left, right, top, bottom for viewing frustrums
|
||||
Only need to set min_x, max_x, min_y, max_y for viewing frustrums
|
||||
which are non symmetric about the origin.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# The initializer formats all inputs to torch tensors and broadcasts
|
||||
@@ -437,10 +568,10 @@ class OpenGLOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
znear=znear,
|
||||
zfar=zfar,
|
||||
top=top,
|
||||
bottom=bottom,
|
||||
left=left,
|
||||
right=right,
|
||||
max_y=max_y,
|
||||
min_y=min_y,
|
||||
max_x=max_x,
|
||||
min_x=min_x,
|
||||
scale_xyz=scale_xyz,
|
||||
R=R,
|
||||
T=T,
|
||||
@@ -448,7 +579,7 @@ class OpenGLOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
|
||||
def get_projection_transform(self, **kwargs) -> Transform3d:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Calculate the OpenGL orthographic projection matrix.
|
||||
Calculate the orthographic projection matrix.
|
||||
Use column major order.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
@@ -456,16 +587,16 @@ class OpenGLOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
override the default values set in __init__.
|
||||
Return:
|
||||
P: a Transform3d object which represents a batch of projection
|
||||
matrices of shape (N, 3, 3)
|
||||
matrices of shape (N, 4, 4)
|
||||
|
||||
.. code-block:: python
|
||||
|
||||
scale_x = 2/(right - left)
|
||||
scale_y = 2/(top - bottom)
|
||||
scale_z = 2/(far-near)
|
||||
mid_x = (right + left)/(right - left)
|
||||
mix_y = (top + bottom)/(top - bottom)
|
||||
mid_z = (far + near)/(far−near)
|
||||
scale_x = 2 / (max_x - min_x)
|
||||
scale_y = 2 / (max_y - min_y)
|
||||
scale_z = 2 / (far-near)
|
||||
mid_x = (max_x + min_x) / (max_x - min_x)
|
||||
mix_y = (max_y + min_y) / (max_y - min_y)
|
||||
mid_z = (far + near) / (far−near)
|
||||
|
||||
P = [
|
||||
[scale_x, 0, 0, -mid_x],
|
||||
@@ -476,10 +607,10 @@ class OpenGLOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
znear = kwargs.get("znear", self.znear) # pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
zfar = kwargs.get("zfar", self.zfar) # pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
left = kwargs.get("left", self.left) # pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
right = kwargs.get("right", self.right) # pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
top = kwargs.get("top", self.top) # pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
bottom = kwargs.get("bottom", self.bottom) # pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
max_x = kwargs.get("max_x", self.max_x) # pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
min_x = kwargs.get("min_x", self.min_x) # pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
max_y = kwargs.get("max_y", self.max_y) # pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
min_y = kwargs.get("min_y", self.min_y) # pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
scale_xyz = kwargs.get("scale_xyz", self.scale_xyz) # pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
|
||||
P = torch.zeros((self._N, 4, 4), dtype=torch.float32, device=self.device)
|
||||
@@ -489,10 +620,10 @@ class OpenGLOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
# right handed coordinate system throughout.
|
||||
z_sign = +1.0
|
||||
|
||||
P[:, 0, 0] = (2.0 / (right - left)) * scale_xyz[:, 0]
|
||||
P[:, 1, 1] = (2.0 / (top - bottom)) * scale_xyz[:, 1]
|
||||
P[:, 0, 3] = -(right + left) / (right - left)
|
||||
P[:, 1, 3] = -(top + bottom) / (top - bottom)
|
||||
P[:, 0, 0] = (2.0 / (max_x - min_x)) * scale_xyz[:, 0]
|
||||
P[:, 1, 1] = (2.0 / (max_y - min_y)) * scale_xyz[:, 1]
|
||||
P[:, 0, 3] = -(max_x + min_x) / (max_x - min_x)
|
||||
P[:, 1, 3] = -(max_y + min_y) / (max_y - min_y)
|
||||
P[:, 3, 3] = ones
|
||||
|
||||
# NOTE: This maps the z coordinate to the range [0, 1] and replaces the
|
||||
@@ -500,12 +631,6 @@ class OpenGLOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
P[:, 2, 2] = z_sign * (1.0 / (zfar - znear)) * scale_xyz[:, 2]
|
||||
P[:, 2, 3] = -znear / (zfar - znear)
|
||||
|
||||
# NOTE: This part of the matrix is for z renormalization in OpenGL.
|
||||
# The z is mapped to the range [-1, 1] but this won't work yet in
|
||||
# pytorch3d as the rasterizer ignores faces which have z < 0.
|
||||
# P[:, 2, 2] = z_sign * (2.0 / (far - near)) * scale[:, 2]
|
||||
# P[:, 2, 3] = -(far + near) / (far - near)
|
||||
|
||||
transform = Transform3d(device=self.device)
|
||||
transform._matrix = P.transpose(1, 2).contiguous()
|
||||
return transform
|
||||
@@ -518,7 +643,7 @@ class OpenGLOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
**kwargs
|
||||
) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
""">!
|
||||
OpenGL cameras further allow for passing depth in world units
|
||||
FoV cameras further allow for passing depth in world units
|
||||
(`scaled_depth_input=False`) or in the [0, 1]-normalized units
|
||||
(`scaled_depth_input=True`)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -529,9 +654,9 @@ class OpenGLOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
if world_coordinates:
|
||||
to_screen_transform = self.get_full_projection_transform(**kwargs.copy())
|
||||
to_ndc_transform = self.get_full_projection_transform(**kwargs.copy())
|
||||
else:
|
||||
to_screen_transform = self.get_projection_transform(**kwargs.copy())
|
||||
to_ndc_transform = self.get_projection_transform(**kwargs.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
if scaled_depth_input:
|
||||
# the input depth is already scaled
|
||||
@@ -547,22 +672,88 @@ class OpenGLOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
# cat xy and scaled depth
|
||||
xy_sdepth = torch.cat((xy_depth[..., :2], scaled_depth), dim=-1)
|
||||
# finally invert the transform
|
||||
unprojection_transform = to_screen_transform.inverse()
|
||||
unprojection_transform = to_ndc_transform.inverse()
|
||||
return unprojection_transform.transform_points(xy_sdepth)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class SfMPerspectiveCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# MultiView Camera Classes #
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Note that the MultiView Cameras accept parameters in both
|
||||
screen and NDC space.
|
||||
If the user specifies `image_size` at construction time then
|
||||
we assume the parameters are in screen space.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def SfMPerspectiveCameras(
|
||||
focal_length=1.0, principal_point=((0.0, 0.0),), R=r, T=t, device="cpu"
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
SfMPerspectiveCameras has been DEPRECATED. Use PerspectiveCameras instead.
|
||||
Preserving SfMPerspectiveCameras for backward compatibility.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
warnings.warn(
|
||||
"""SfMPerspectiveCameras is deprecated,
|
||||
Use PerspectiveCameras instead.
|
||||
SfMPerspectiveCameras will be removed in future releases.""",
|
||||
PendingDeprecationWarning,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return PerspectiveCameras(
|
||||
focal_length=focal_length,
|
||||
principal_point=principal_point,
|
||||
R=R,
|
||||
T=T,
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PerspectiveCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A class which stores a batch of parameters to generate a batch of
|
||||
transformation matrices using the multi-view geometry convention for
|
||||
perspective camera.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters for this camera can be specified in NDC or in screen space.
|
||||
If you wish to provide parameters in screen space, you NEED to provide
|
||||
the image_size = (imwidth, imheight).
|
||||
If you wish to provide parameters in NDC space, you should NOT provide
|
||||
image_size. Providing valid image_size will triger a screen space to
|
||||
NDC space transformation in the camera.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, here is how to define cameras on the two spaces.
|
||||
|
||||
.. code-block:: python
|
||||
# camera defined in screen space
|
||||
cameras = PerspectiveCameras(
|
||||
focal_length=((22.0, 15.0),), # (fx_screen, fy_screen)
|
||||
principal_point=((192.0, 128.0),), # (px_screen, py_screen)
|
||||
image_size=((256, 256),), # (imwidth, imheight)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# the equivalent camera defined in NDC space
|
||||
cameras = PerspectiveCameras(
|
||||
focal_length=((0.17875, 0.11718),), # fx = fx_screen / half_imwidth,
|
||||
# fy = fy_screen / half_imheight
|
||||
principal_point=((-0.5, 0),), # px = - (px_screen - half_imwidth) / half_imwidth,
|
||||
# py = - (py_screen - half_imheight) / half_imheight
|
||||
)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self, focal_length=1.0, principal_point=((0.0, 0.0),), R=r, T=t, device="cpu"
|
||||
self,
|
||||
focal_length=1.0,
|
||||
principal_point=((0.0, 0.0),),
|
||||
R=r,
|
||||
T=t,
|
||||
device="cpu",
|
||||
image_size=((-1, -1),),
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
__init__(self, focal_length, principal_point, R, T, device) -> None
|
||||
__init__(self, focal_length, principal_point, R, T, device, image_size) -> None
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
focal_length: Focal length of the camera in world units.
|
||||
@@ -574,6 +765,11 @@ class SfMPerspectiveCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
R: Rotation matrix of shape (N, 3, 3)
|
||||
T: Translation matrix of shape (N, 3)
|
||||
device: torch.device or string
|
||||
image_size: If image_size = (imwidth, imheight) with imwidth, imheight > 0
|
||||
is provided, the camera parameters are assumed to be in screen
|
||||
space. They will be converted to NDC space.
|
||||
If image_size is not provided, the parameters are assumed to
|
||||
be in NDC space.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# The initializer formats all inputs to torch tensors and broadcasts
|
||||
# all the inputs to have the same batch dimension where necessary.
|
||||
@@ -583,6 +779,7 @@ class SfMPerspectiveCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
principal_point=principal_point,
|
||||
R=R,
|
||||
T=T,
|
||||
image_size=image_size,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def get_projection_transform(self, **kwargs) -> Transform3d:
|
||||
@@ -615,9 +812,20 @@ class SfMPerspectiveCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
principal_point = kwargs.get("principal_point", self.principal_point)
|
||||
# pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
focal_length = kwargs.get("focal_length", self.focal_length)
|
||||
# pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
image_size = kwargs.get("image_size", self.image_size)
|
||||
|
||||
# if imwidth > 0, parameters are in screen space
|
||||
in_screen = image_size[0][0] > 0
|
||||
image_size = image_size if in_screen else None
|
||||
|
||||
P = _get_sfm_calibration_matrix(
|
||||
self._N, self.device, focal_length, principal_point, False
|
||||
self._N,
|
||||
self.device,
|
||||
focal_length,
|
||||
principal_point,
|
||||
orthographic=False,
|
||||
image_size=image_size,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
transform = Transform3d(device=self.device)
|
||||
@@ -628,29 +836,83 @@ class SfMPerspectiveCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
self, xy_depth: torch.Tensor, world_coordinates: bool = True, **kwargs
|
||||
) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
if world_coordinates:
|
||||
to_screen_transform = self.get_full_projection_transform(**kwargs)
|
||||
to_ndc_transform = self.get_full_projection_transform(**kwargs)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
to_screen_transform = self.get_projection_transform(**kwargs)
|
||||
to_ndc_transform = self.get_projection_transform(**kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
unprojection_transform = to_screen_transform.inverse()
|
||||
unprojection_transform = to_ndc_transform.inverse()
|
||||
xy_inv_depth = torch.cat(
|
||||
(xy_depth[..., :2], 1.0 / xy_depth[..., 2:3]), dim=-1 # type: ignore
|
||||
)
|
||||
return unprojection_transform.transform_points(xy_inv_depth)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class SfMOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
def SfMOrthographicCameras(
|
||||
focal_length=1.0, principal_point=((0.0, 0.0),), R=r, T=t, device="cpu"
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
SfMOrthographicCameras has been DEPRECATED. Use OrthographicCameras instead.
|
||||
Preserving SfMOrthographicCameras for backward compatibility.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
warnings.warn(
|
||||
"""SfMOrthographicCameras is deprecated,
|
||||
Use OrthographicCameras instead.
|
||||
SfMOrthographicCameras will be removed in future releases.""",
|
||||
PendingDeprecationWarning,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return OrthographicCameras(
|
||||
focal_length=focal_length,
|
||||
principal_point=principal_point,
|
||||
R=R,
|
||||
T=T,
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class OrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A class which stores a batch of parameters to generate a batch of
|
||||
transformation matrices using the multi-view geometry convention for
|
||||
orthographic camera.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters for this camera can be specified in NDC or in screen space.
|
||||
If you wish to provide parameters in screen space, you NEED to provide
|
||||
the image_size = (imwidth, imheight).
|
||||
If you wish to provide parameters in NDC space, you should NOT provide
|
||||
image_size. Providing valid image_size will triger a screen space to
|
||||
NDC space transformation in the camera.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, here is how to define cameras on the two spaces.
|
||||
|
||||
.. code-block:: python
|
||||
# camera defined in screen space
|
||||
cameras = OrthographicCameras(
|
||||
focal_length=((22.0, 15.0),), # (fx, fy)
|
||||
principal_point=((192.0, 128.0),), # (px, py)
|
||||
image_size=((256, 256),), # (imwidth, imheight)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# the equivalent camera defined in NDC space
|
||||
cameras = OrthographicCameras(
|
||||
focal_length=((0.17875, 0.11718),), # := (fx / half_imwidth, fy / half_imheight)
|
||||
principal_point=((-0.5, 0),), # := (- (px - half_imwidth) / half_imwidth,
|
||||
- (py - half_imheight) / half_imheight)
|
||||
)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self, focal_length=1.0, principal_point=((0.0, 0.0),), R=r, T=t, device="cpu"
|
||||
self,
|
||||
focal_length=1.0,
|
||||
principal_point=((0.0, 0.0),),
|
||||
R=r,
|
||||
T=t,
|
||||
device="cpu",
|
||||
image_size=((-1, -1),),
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
__init__(self, focal_length, principal_point, R, T, device) -> None
|
||||
__init__(self, focal_length, principal_point, R, T, device, image_size) -> None
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
focal_length: Focal length of the camera in world units.
|
||||
@@ -662,6 +924,11 @@ class SfMOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
R: Rotation matrix of shape (N, 3, 3)
|
||||
T: Translation matrix of shape (N, 3)
|
||||
device: torch.device or string
|
||||
image_size: If image_size = (imwidth, imheight) with imwidth, imheight > 0
|
||||
is provided, the camera parameters are assumed to be in screen
|
||||
space. They will be converted to NDC space.
|
||||
If image_size is not provided, the parameters are assumed to
|
||||
be in NDC space.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# The initializer formats all inputs to torch tensors and broadcasts
|
||||
# all the inputs to have the same batch dimension where necessary.
|
||||
@@ -671,6 +938,7 @@ class SfMOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
principal_point=principal_point,
|
||||
R=R,
|
||||
T=T,
|
||||
image_size=image_size,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def get_projection_transform(self, **kwargs) -> Transform3d:
|
||||
@@ -703,9 +971,20 @@ class SfMOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
principal_point = kwargs.get("principal_point", self.principal_point)
|
||||
# pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
focal_length = kwargs.get("focal_length", self.focal_length)
|
||||
# pyre-ignore[16]
|
||||
image_size = kwargs.get("image_size", self.image_size)
|
||||
|
||||
# if imwidth > 0, parameters are in screen space
|
||||
in_screen = image_size[0][0] > 0
|
||||
image_size = image_size if in_screen else None
|
||||
|
||||
P = _get_sfm_calibration_matrix(
|
||||
self._N, self.device, focal_length, principal_point, True
|
||||
self._N,
|
||||
self.device,
|
||||
focal_length,
|
||||
principal_point,
|
||||
orthographic=True,
|
||||
image_size=image_size,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
transform = Transform3d(device=self.device)
|
||||
@@ -716,17 +995,26 @@ class SfMOrthographicCameras(CamerasBase):
|
||||
self, xy_depth: torch.Tensor, world_coordinates: bool = True, **kwargs
|
||||
) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
if world_coordinates:
|
||||
to_screen_transform = self.get_full_projection_transform(**kwargs)
|
||||
to_ndc_transform = self.get_full_projection_transform(**kwargs)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
to_screen_transform = self.get_projection_transform(**kwargs)
|
||||
to_ndc_transform = self.get_projection_transform(**kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
unprojection_transform = to_screen_transform.inverse()
|
||||
unprojection_transform = to_ndc_transform.inverse()
|
||||
return unprojection_transform.transform_points(xy_depth)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# SfMCameras helper
|
||||
################################################
|
||||
# Helper functions for cameras #
|
||||
################################################
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_sfm_calibration_matrix(
|
||||
N, device, focal_length, principal_point, orthographic: bool
|
||||
N,
|
||||
device,
|
||||
focal_length,
|
||||
principal_point,
|
||||
orthographic: bool = False,
|
||||
image_size=None,
|
||||
) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a calibration matrix of a perspective/orthograpic camera.
|
||||
@@ -736,6 +1024,10 @@ def _get_sfm_calibration_matrix(
|
||||
focal_length: Focal length of the camera in world units.
|
||||
principal_point: xy coordinates of the center of
|
||||
the principal point of the camera in pixels.
|
||||
orthographic: Boolean specifying if the camera is orthographic or not
|
||||
image_size: (Optional) Specifying the image_size = (imwidth, imheight).
|
||||
If not None, the camera parameters are assumed to be in screen space
|
||||
and are transformed to NDC space.
|
||||
|
||||
The calibration matrix `K` is set up as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -769,7 +1061,7 @@ def _get_sfm_calibration_matrix(
|
||||
if not torch.is_tensor(focal_length):
|
||||
focal_length = torch.tensor(focal_length, device=device)
|
||||
|
||||
if len(focal_length.shape) in (0, 1) or focal_length.shape[1] == 1:
|
||||
if focal_length.ndim in (0, 1) or focal_length.shape[1] == 1:
|
||||
fx = fy = focal_length
|
||||
else:
|
||||
fx, fy = focal_length.unbind(1)
|
||||
@@ -779,6 +1071,22 @@ def _get_sfm_calibration_matrix(
|
||||
|
||||
px, py = principal_point.unbind(1)
|
||||
|
||||
if image_size is not None:
|
||||
if not torch.is_tensor(image_size):
|
||||
image_size = torch.tensor(image_size, device=device)
|
||||
imwidth, imheight = image_size.unbind(1)
|
||||
# make sure imwidth, imheight are valid (>0)
|
||||
if (imwidth < 1).any() or (imheight < 1).any():
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"Camera parameters provided in screen space. Image width or height invalid."
|
||||
)
|
||||
half_imwidth = imwidth / 2.0
|
||||
half_imheight = imheight / 2.0
|
||||
fx = fx / half_imwidth
|
||||
fy = fy / half_imheight
|
||||
px = -(px - half_imwidth) / half_imwidth
|
||||
py = -(py - half_imheight) / half_imheight
|
||||
|
||||
K = fx.new_zeros(N, 4, 4)
|
||||
K[:, 0, 0] = fx
|
||||
K[:, 1, 1] = fy
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ from itertools import product
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from fvcore.common.benchmark import benchmark
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import OpenGLPerspectiveCameras, look_at_view_transform
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import FoVPerspectiveCameras, look_at_view_transform
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.mesh.rasterizer import (
|
||||
Fragments,
|
||||
MeshRasterizer,
|
||||
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ def baryclip_cuda(
|
||||
sphere_meshes = ico_sphere(ico_level, device).extend(num_meshes)
|
||||
# Init transform
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(1.0, 0.0, 0.0)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
# Init rasterizer
|
||||
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(
|
||||
image_size=image_size,
|
||||
@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ def baryclip_pytorch(
|
||||
sphere_meshes = ico_sphere(ico_level, device).extend(num_meshes)
|
||||
# Init transform
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(1.0, 0.0, 0.0)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
# Init rasterizer
|
||||
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(
|
||||
image_size=image_size,
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ from itertools import product
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from fvcore.common.benchmark import benchmark
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import OpenGLPerspectiveCameras, look_at_view_transform
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import FoVPerspectiveCameras, look_at_view_transform
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.mesh.rasterizer import MeshRasterizer
|
||||
from pytorch3d.utils.ico_sphere import ico_sphere
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ def rasterize_transform_with_init(num_meshes: int, ico_level: int = 5, device="c
|
||||
sphere_meshes = ico_sphere(ico_level, device).extend(num_meshes)
|
||||
# Init transform
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(1.0, 0.0, 0.0)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
# Init rasterizer
|
||||
rasterizer = MeshRasterizer(cameras=cameras)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
BIN
tests/data/test_FoVOrthographicCameras_silhouette.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 48 KiB |
BIN
tests/data/test_FoVPerspectiveCameras_silhouette.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 8.7 KiB |
BIN
tests/data/test_OrthographicCameras_silhouette.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 48 KiB |
BIN
tests/data/test_PerspectiveCameras_silhouette.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 5.5 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 8.8 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 26 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 18 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 18 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 3.4 KiB |
BIN
tests/data/test_simple_sphere_dark_FoVOrthographicCameras.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 3.7 KiB |
BIN
tests/data/test_simple_sphere_dark_FoVPerspectiveCameras.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 2.8 KiB |
BIN
tests/data/test_simple_sphere_dark_OrthographicCameras.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 3.7 KiB |
BIN
tests/data/test_simple_sphere_dark_PerspectiveCameras.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 2.0 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 7.8 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 3.8 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 7.8 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 2.5 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 3.8 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 26 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 34 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 26 KiB |
BIN
tests/data/test_simple_sphere_light_flat_OrthographicCameras.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 34 KiB |
BIN
tests/data/test_simple_sphere_light_flat_PerspectiveCameras.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 13 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 25 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 15 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 25 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 8.5 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 15 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 18 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 23 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 18 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 23 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 9.1 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 17 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 10 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 17 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 5.8 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 10 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 21 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 22 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 18 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 22 KiB |
BIN
tests/data/test_simple_sphere_light_phong_PerspectiveCameras.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 8.8 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 16 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 10 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 16 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 5.6 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 10 KiB |
@@ -31,12 +31,16 @@ import unittest
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from common_testing import TestCaseMixin
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import OpenGLOrthographicCameras # deprecated
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import OpenGLPerspectiveCameras # deprecated
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import SfMOrthographicCameras # deprecated
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import SfMPerspectiveCameras # deprecated
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import (
|
||||
CamerasBase,
|
||||
OpenGLOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
OpenGLPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
SfMOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
SfMPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
FoVOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
OrthographicCameras,
|
||||
PerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
camera_position_from_spherical_angles,
|
||||
get_world_to_view_transform,
|
||||
look_at_rotation,
|
||||
@@ -109,6 +113,25 @@ def orthographic_project_naive(points, scale_xyz=(1.0, 1.0, 1.0)):
|
||||
return points
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def ndc_to_screen_points_naive(points, imsize):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Transforms points from PyTorch3D's NDC space to screen space
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
points: (N, V, 3) representing padded points
|
||||
imsize: (N, 2) image size = (width, height)
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
(N, V, 3) tensor of transformed points
|
||||
"""
|
||||
imwidth, imheight = imsize.unbind(1)
|
||||
imwidth = imwidth.view(-1, 1)
|
||||
imheight = imheight.view(-1, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
x, y, z = points.unbind(2)
|
||||
x = (1.0 - x) * (imwidth - 1) / 2.0
|
||||
y = (1.0 - y) * (imheight - 1) / 2.0
|
||||
return torch.stack((x, y, z), dim=2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestCameraHelpers(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def setUp(self) -> None:
|
||||
super().setUp()
|
||||
@@ -359,6 +382,10 @@ class TestCamerasCommon(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
OpenGLOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
SfMOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
SfMPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
FoVOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
OrthographicCameras,
|
||||
PerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
):
|
||||
cam = cam_type(R=R, T=T)
|
||||
RT_class = cam.get_world_to_view_transform()
|
||||
@@ -374,6 +401,10 @@ class TestCamerasCommon(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
OpenGLOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
SfMOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
SfMPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
FoVOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
OrthographicCameras,
|
||||
PerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
):
|
||||
cam = cam_type(R=R, T=T)
|
||||
C = cam.get_camera_center()
|
||||
@@ -398,13 +429,53 @@ class TestCamerasCommon(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
cam_params["bottom"] = -(torch.rand(batch_size)) * 0.2 - 0.9
|
||||
cam_params["left"] = -(torch.rand(batch_size)) * 0.2 - 0.9
|
||||
cam_params["right"] = torch.rand(batch_size) * 0.2 + 0.9
|
||||
elif cam_type in (SfMOrthographicCameras, SfMPerspectiveCameras):
|
||||
elif cam_type in (FoVPerspectiveCameras, FoVOrthographicCameras):
|
||||
cam_params["znear"] = torch.rand(batch_size) * 10 + 0.1
|
||||
cam_params["zfar"] = torch.rand(batch_size) * 4 + 1 + cam_params["znear"]
|
||||
if cam_type == FoVPerspectiveCameras:
|
||||
cam_params["fov"] = torch.rand(batch_size) * 60 + 30
|
||||
cam_params["aspect_ratio"] = torch.rand(batch_size) * 0.5 + 0.5
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cam_params["max_y"] = torch.rand(batch_size) * 0.2 + 0.9
|
||||
cam_params["min_y"] = -(torch.rand(batch_size)) * 0.2 - 0.9
|
||||
cam_params["min_x"] = -(torch.rand(batch_size)) * 0.2 - 0.9
|
||||
cam_params["max_x"] = torch.rand(batch_size) * 0.2 + 0.9
|
||||
elif cam_type in (
|
||||
SfMOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
SfMPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
OrthographicCameras,
|
||||
PerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
):
|
||||
cam_params["focal_length"] = torch.rand(batch_size) * 10 + 0.1
|
||||
cam_params["principal_point"] = torch.randn((batch_size, 2))
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError(str(cam_type))
|
||||
return cam_type(**cam_params)
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def init_equiv_cameras_ndc_screen(cam_type: CamerasBase, batch_size: int):
|
||||
T = torch.randn(batch_size, 3) * 0.03
|
||||
T[:, 2] = 4
|
||||
R = so3_exponential_map(torch.randn(batch_size, 3) * 3.0)
|
||||
screen_cam_params = {"R": R, "T": T}
|
||||
ndc_cam_params = {"R": R, "T": T}
|
||||
if cam_type in (OrthographicCameras, PerspectiveCameras):
|
||||
ndc_cam_params["focal_length"] = torch.rand((batch_size, 2)) * 3.0
|
||||
ndc_cam_params["principal_point"] = torch.randn((batch_size, 2))
|
||||
|
||||
image_size = torch.randint(low=2, high=64, size=(batch_size, 2))
|
||||
screen_cam_params["image_size"] = image_size
|
||||
screen_cam_params["focal_length"] = (
|
||||
ndc_cam_params["focal_length"] * image_size / 2.0
|
||||
)
|
||||
screen_cam_params["principal_point"] = (
|
||||
(1.0 - ndc_cam_params["principal_point"]) * image_size / 2.0
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError(str(cam_type))
|
||||
return cam_type(**ndc_cam_params), cam_type(**screen_cam_params)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_unproject_points(self, batch_size=50, num_points=100):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Checks that an unprojection of a randomly projected point cloud
|
||||
@@ -416,6 +487,10 @@ class TestCamerasCommon(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
OpenGLPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
OpenGLOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
SfMPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
FoVOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
OrthographicCameras,
|
||||
PerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
):
|
||||
# init the cameras
|
||||
cameras = TestCamerasCommon.init_random_cameras(cam_type, batch_size)
|
||||
@@ -437,9 +512,14 @@ class TestCamerasCommon(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
else:
|
||||
matching_xyz = xyz_cam
|
||||
|
||||
# if we have OpenGL cameras
|
||||
# if we have FoV (= OpenGL) cameras
|
||||
# test for scaled_depth_input=True/False
|
||||
if cam_type in (OpenGLPerspectiveCameras, OpenGLOrthographicCameras):
|
||||
if cam_type in (
|
||||
OpenGLPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
OpenGLOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
FoVOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
):
|
||||
for scaled_depth_input in (True, False):
|
||||
if scaled_depth_input:
|
||||
xy_depth_ = xyz_proj
|
||||
@@ -459,6 +539,56 @@ class TestCamerasCommon(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(torch.allclose(xyz_unproj, matching_xyz, atol=1e-4))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_project_points_screen(self, batch_size=50, num_points=100):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Checks that an unprojection of a randomly projected point cloud
|
||||
stays the same.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
for cam_type in (
|
||||
OpenGLOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
OpenGLPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
SfMOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
SfMPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
FoVOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
OrthographicCameras,
|
||||
PerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
):
|
||||
|
||||
# init the cameras
|
||||
cameras = TestCamerasCommon.init_random_cameras(cam_type, batch_size)
|
||||
# xyz - the ground truth point cloud
|
||||
xyz = torch.randn(batch_size, num_points, 3) * 0.3
|
||||
# image size
|
||||
image_size = torch.randint(low=2, high=64, size=(batch_size, 2))
|
||||
# project points
|
||||
xyz_project_ndc = cameras.transform_points(xyz)
|
||||
xyz_project_screen = cameras.transform_points_screen(xyz, image_size)
|
||||
# naive
|
||||
xyz_project_screen_naive = ndc_to_screen_points_naive(
|
||||
xyz_project_ndc, image_size
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.assertClose(xyz_project_screen, xyz_project_screen_naive)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_equiv_project_points(self, batch_size=50, num_points=100):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Checks that NDC and screen cameras project points to ndc correctly.
|
||||
Applies only to OrthographicCameras and PerspectiveCameras.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
for cam_type in (OrthographicCameras, PerspectiveCameras):
|
||||
# init the cameras
|
||||
(
|
||||
ndc_cameras,
|
||||
screen_cameras,
|
||||
) = TestCamerasCommon.init_equiv_cameras_ndc_screen(cam_type, batch_size)
|
||||
# xyz - the ground truth point cloud
|
||||
xyz = torch.randn(batch_size, num_points, 3) * 0.3
|
||||
# project points
|
||||
xyz_ndc_cam = ndc_cameras.transform_points(xyz)
|
||||
xyz_screen_cam = screen_cameras.transform_points(xyz)
|
||||
self.assertClose(xyz_ndc_cam, xyz_screen_cam, atol=1e-6)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_clone(self, batch_size: int = 10):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Checks the clone function of the cameras.
|
||||
@@ -468,6 +598,10 @@ class TestCamerasCommon(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
OpenGLPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
OpenGLOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
SfMPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
FoVOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
OrthographicCameras,
|
||||
PerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
):
|
||||
cameras = TestCamerasCommon.init_random_cameras(cam_type, batch_size)
|
||||
cameras = cameras.to(torch.device("cpu"))
|
||||
@@ -483,11 +617,16 @@ class TestCamerasCommon(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertTrue(val == val_clone)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestPerspectiveProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# FoVPerspective Camera #
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestFoVPerspectiveProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def test_perspective(self):
|
||||
far = 10.0
|
||||
near = 1.0
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(znear=near, zfar=far, fov=60.0)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(znear=near, zfar=far, fov=60.0)
|
||||
P = cameras.get_projection_transform()
|
||||
# vertices are at the far clipping plane so z gets mapped to 1.
|
||||
vertices = torch.tensor([1, 2, far], dtype=torch.float32)
|
||||
@@ -512,7 +651,7 @@ class TestPerspectiveProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertClose(v1.squeeze(), projected_verts)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_perspective_kwargs(self):
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(znear=5.0, zfar=100.0, fov=0.0)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(znear=5.0, zfar=100.0, fov=0.0)
|
||||
# Override defaults by passing in values to get_projection_transform
|
||||
far = 10.0
|
||||
P = cameras.get_projection_transform(znear=1.0, zfar=far, fov=60.0)
|
||||
@@ -528,7 +667,7 @@ class TestPerspectiveProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
far = torch.tensor([10.0, 20.0], dtype=torch.float32)
|
||||
near = 1.0
|
||||
fov = torch.tensor(60.0)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(znear=near, zfar=far, fov=fov)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(znear=near, zfar=far, fov=fov)
|
||||
P = cameras.get_projection_transform()
|
||||
vertices = torch.tensor([1, 2, 10], dtype=torch.float32)
|
||||
z1 = 1.0 # vertices at far clipping plane so z = 1.0
|
||||
@@ -550,7 +689,7 @@ class TestPerspectiveProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
far = torch.tensor([10.0])
|
||||
near = 1.0
|
||||
fov = torch.tensor(60.0, requires_grad=True)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(znear=near, zfar=far, fov=fov)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(znear=near, zfar=far, fov=fov)
|
||||
P = cameras.get_projection_transform()
|
||||
vertices = torch.tensor([1, 2, 10], dtype=torch.float32)
|
||||
vertices_batch = vertices[None, None, :]
|
||||
@@ -566,7 +705,7 @@ class TestPerspectiveProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def test_camera_class_init(self):
|
||||
device = torch.device("cuda:0")
|
||||
cam = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(znear=10.0, zfar=(100.0, 200.0))
|
||||
cam = FoVPerspectiveCameras(znear=10.0, zfar=(100.0, 200.0))
|
||||
|
||||
# Check broadcasting
|
||||
self.assertTrue(cam.znear.shape == (2,))
|
||||
@@ -585,7 +724,7 @@ class TestPerspectiveProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertTrue(new_cam.device == device)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_get_full_transform(self):
|
||||
cam = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras()
|
||||
cam = FoVPerspectiveCameras()
|
||||
T = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 1.0]).view(1, -1)
|
||||
R = look_at_rotation(T)
|
||||
P = cam.get_full_projection_transform(R=R, T=T)
|
||||
@@ -597,7 +736,7 @@ class TestPerspectiveProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
# Check transform_points methods works with default settings for
|
||||
# RT and P
|
||||
far = 10.0
|
||||
cam = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(znear=1.0, zfar=far, fov=60.0)
|
||||
cam = FoVPerspectiveCameras(znear=1.0, zfar=far, fov=60.0)
|
||||
points = torch.tensor([1, 2, far], dtype=torch.float32)
|
||||
points = points.view(1, 1, 3).expand(5, 10, -1)
|
||||
projected_points = torch.tensor(
|
||||
@@ -608,11 +747,16 @@ class TestPerspectiveProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertClose(new_points, projected_points)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestOpenGLOrthographicProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# FoVOrthographic Camera #
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestFoVOrthographicProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def test_orthographic(self):
|
||||
far = 10.0
|
||||
near = 1.0
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLOrthographicCameras(znear=near, zfar=far)
|
||||
cameras = FoVOrthographicCameras(znear=near, zfar=far)
|
||||
P = cameras.get_projection_transform()
|
||||
|
||||
vertices = torch.tensor([1, 2, far], dtype=torch.float32)
|
||||
@@ -637,7 +781,7 @@ class TestOpenGLOrthographicProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
# applying the scale puts the z coordinate at the far clipping plane
|
||||
# so the z is mapped to 1.0
|
||||
projected_verts = torch.tensor([2, 1, 1], dtype=torch.float32)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLOrthographicCameras(znear=1.0, zfar=10.0, scale_xyz=scale)
|
||||
cameras = FoVOrthographicCameras(znear=1.0, zfar=10.0, scale_xyz=scale)
|
||||
P = cameras.get_projection_transform()
|
||||
v1 = P.transform_points(vertices)
|
||||
v2 = orthographic_project_naive(vertices, scale)
|
||||
@@ -645,7 +789,7 @@ class TestOpenGLOrthographicProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertClose(v1, projected_verts[None, None])
|
||||
|
||||
def test_orthographic_kwargs(self):
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLOrthographicCameras(znear=5.0, zfar=100.0)
|
||||
cameras = FoVOrthographicCameras(znear=5.0, zfar=100.0)
|
||||
far = 10.0
|
||||
P = cameras.get_projection_transform(znear=1.0, zfar=far)
|
||||
vertices = torch.tensor([1, 2, far], dtype=torch.float32)
|
||||
@@ -657,7 +801,7 @@ class TestOpenGLOrthographicProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def test_orthographic_mixed_inputs_broadcast(self):
|
||||
far = torch.tensor([10.0, 20.0])
|
||||
near = 1.0
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLOrthographicCameras(znear=near, zfar=far)
|
||||
cameras = FoVOrthographicCameras(znear=near, zfar=far)
|
||||
P = cameras.get_projection_transform()
|
||||
vertices = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 10.0], dtype=torch.float32)
|
||||
z2 = 1.0 / (20.0 - 1.0) * 10.0 + -1.0 / (20.0 - 1.0)
|
||||
@@ -674,7 +818,7 @@ class TestOpenGLOrthographicProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
far = torch.tensor([10.0])
|
||||
near = 1.0
|
||||
scale = torch.tensor([[1.0, 1.0, 1.0]], requires_grad=True)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLOrthographicCameras(znear=near, zfar=far, scale_xyz=scale)
|
||||
cameras = FoVOrthographicCameras(znear=near, zfar=far, scale_xyz=scale)
|
||||
P = cameras.get_projection_transform()
|
||||
vertices = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 10.0], dtype=torch.float32)
|
||||
vertices_batch = vertices[None, None, :]
|
||||
@@ -694,9 +838,14 @@ class TestOpenGLOrthographicProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertClose(scale_grad, grad_scale)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestSfMOrthographicProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Orthographic Camera #
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestOrthographicProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def test_orthographic(self):
|
||||
cameras = SfMOrthographicCameras()
|
||||
cameras = OrthographicCameras()
|
||||
P = cameras.get_projection_transform()
|
||||
|
||||
vertices = torch.randn([3, 4, 3], dtype=torch.float32)
|
||||
@@ -711,9 +860,7 @@ class TestSfMOrthographicProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
focal_length_x = 10.0
|
||||
focal_length_y = 15.0
|
||||
|
||||
cameras = SfMOrthographicCameras(
|
||||
focal_length=((focal_length_x, focal_length_y),)
|
||||
)
|
||||
cameras = OrthographicCameras(focal_length=((focal_length_x, focal_length_y),))
|
||||
P = cameras.get_projection_transform()
|
||||
|
||||
vertices = torch.randn([3, 4, 3], dtype=torch.float32)
|
||||
@@ -730,9 +877,7 @@ class TestSfMOrthographicProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertClose(v1, projected_verts)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_orthographic_kwargs(self):
|
||||
cameras = SfMOrthographicCameras(
|
||||
focal_length=5.0, principal_point=((2.5, 2.5),)
|
||||
)
|
||||
cameras = OrthographicCameras(focal_length=5.0, principal_point=((2.5, 2.5),))
|
||||
P = cameras.get_projection_transform(
|
||||
focal_length=2.0, principal_point=((2.5, 3.5),)
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -745,9 +890,14 @@ class TestSfMOrthographicProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertClose(v1, projected_verts)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestSfMPerspectiveProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Perspective Camera #
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestPerspectiveProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def test_perspective(self):
|
||||
cameras = SfMPerspectiveCameras()
|
||||
cameras = PerspectiveCameras()
|
||||
P = cameras.get_projection_transform()
|
||||
|
||||
vertices = torch.randn([3, 4, 3], dtype=torch.float32)
|
||||
@@ -761,7 +911,7 @@ class TestSfMPerspectiveProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
p0x = 15.0
|
||||
p0y = 30.0
|
||||
|
||||
cameras = SfMPerspectiveCameras(
|
||||
cameras = PerspectiveCameras(
|
||||
focal_length=((focal_length_x, focal_length_y),),
|
||||
principal_point=((p0x, p0y),),
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -777,7 +927,7 @@ class TestSfMPerspectiveProjection(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertClose(v3[..., :2], v2[..., :2])
|
||||
|
||||
def test_perspective_kwargs(self):
|
||||
cameras = SfMPerspectiveCameras(focal_length=5.0, principal_point=((2.5, 2.5),))
|
||||
cameras = PerspectiveCameras(focal_length=5.0, principal_point=((2.5, 2.5),))
|
||||
P = cameras.get_projection_transform(
|
||||
focal_length=2.0, principal_point=((2.5, 3.5),)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ from pytorch3d.datasets import (
|
||||
render_cubified_voxels,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer import (
|
||||
OpenGLPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
PointLights,
|
||||
RasterizationSettings,
|
||||
look_at_view_transform,
|
||||
@@ -211,7 +211,7 @@ class TestR2N2(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
# Render first three models in the dataset.
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(1.0, 1.0, 90)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(R=R, T=T, device=device)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(R=R, T=T, device=device)
|
||||
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(image_size=512)
|
||||
lights = PointLights(
|
||||
location=torch.tensor([0.0, 1.0, -2.0], device=device)[None],
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ from pathlib import Path
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import OpenGLPerspectiveCameras, look_at_view_transform
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import FoVPerspectiveCameras, look_at_view_transform
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.mesh.rasterizer import MeshRasterizer, RasterizationSettings
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.points.rasterizer import (
|
||||
PointsRasterizationSettings,
|
||||
@@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ class TestMeshRasterizer(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
# Init rasterizer settings
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(2.7, 0, 0)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(
|
||||
image_size=512, blur_radius=0.0, faces_per_pixel=1, bin_size=0
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -148,7 +148,7 @@ class TestPointRasterizer(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
verts_padded[..., 0] += 0.2
|
||||
pointclouds = Pointclouds(points=verts_padded)
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(2.7, 0.0, 0.0)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
raster_settings = PointsRasterizationSettings(
|
||||
image_size=256, radius=5e-2, points_per_pixel=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,6 +4,7 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Sanity checks for output images from the renderer.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import unittest
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,7 +13,13 @@ import torch
|
||||
from common_testing import TestCaseMixin, load_rgb_image
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from pytorch3d.io import load_obj
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import OpenGLPerspectiveCameras, look_at_view_transform
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import (
|
||||
FoVOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
OrthographicCameras,
|
||||
PerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
look_at_view_transform,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.lighting import PointLights
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.materials import Materials
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.mesh import TexturesAtlas, TexturesUV, TexturesVertex
|
||||
@@ -60,78 +67,94 @@ class TestRenderMeshes(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
if elevated_camera:
|
||||
# Elevated and rotated camera
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(dist=2.7, elev=45.0, azim=45.0)
|
||||
postfix = "_elevated_camera"
|
||||
postfix = "_elevated_"
|
||||
# If y axis is up, the spot of light should
|
||||
# be on the bottom left of the sphere.
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# No elevation or azimuth rotation
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(2.7, 0.0, 0.0)
|
||||
postfix = ""
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
postfix = "_"
|
||||
for cam_type in (
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
FoVOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
PerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
OrthographicCameras,
|
||||
):
|
||||
cameras = cam_type(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
|
||||
# Init shader settings
|
||||
materials = Materials(device=device)
|
||||
lights = PointLights(device=device)
|
||||
lights.location = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, +2.0], device=device)[None]
|
||||
# Init shader settings
|
||||
materials = Materials(device=device)
|
||||
lights = PointLights(device=device)
|
||||
lights.location = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, +2.0], device=device)[None]
|
||||
|
||||
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(
|
||||
image_size=512, blur_radius=0.0, faces_per_pixel=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
rasterizer = MeshRasterizer(cameras=cameras, raster_settings=raster_settings)
|
||||
blend_params = BlendParams(1e-4, 1e-4, (0, 0, 0))
|
||||
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(
|
||||
image_size=512, blur_radius=0.0, faces_per_pixel=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
rasterizer = MeshRasterizer(
|
||||
cameras=cameras, raster_settings=raster_settings
|
||||
)
|
||||
blend_params = BlendParams(1e-4, 1e-4, (0, 0, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
# Test several shaders
|
||||
shaders = {
|
||||
"phong": HardPhongShader,
|
||||
"gouraud": HardGouraudShader,
|
||||
"flat": HardFlatShader,
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (name, shader_init) in shaders.items():
|
||||
shader = shader_init(
|
||||
# Test several shaders
|
||||
shaders = {
|
||||
"phong": HardPhongShader,
|
||||
"gouraud": HardGouraudShader,
|
||||
"flat": HardFlatShader,
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (name, shader_init) in shaders.items():
|
||||
shader = shader_init(
|
||||
lights=lights,
|
||||
cameras=cameras,
|
||||
materials=materials,
|
||||
blend_params=blend_params,
|
||||
)
|
||||
renderer = MeshRenderer(rasterizer=rasterizer, shader=shader)
|
||||
images = renderer(sphere_mesh)
|
||||
rgb = images[0, ..., :3].squeeze().cpu()
|
||||
filename = "simple_sphere_light_%s%s%s.png" % (
|
||||
name,
|
||||
postfix,
|
||||
cam_type.__name__,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
image_ref = load_rgb_image("test_%s" % filename, DATA_DIR)
|
||||
self.assertClose(rgb, image_ref, atol=0.05)
|
||||
|
||||
if DEBUG:
|
||||
filename = "DEBUG_%s" % filename
|
||||
Image.fromarray((rgb.numpy() * 255).astype(np.uint8)).save(
|
||||
DATA_DIR / filename
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
########################################################
|
||||
# Move the light to the +z axis in world space so it is
|
||||
# behind the sphere. Note that +Z is in, +Y up,
|
||||
# +X left for both world and camera space.
|
||||
########################################################
|
||||
lights.location[..., 2] = -2.0
|
||||
phong_shader = HardPhongShader(
|
||||
lights=lights,
|
||||
cameras=cameras,
|
||||
materials=materials,
|
||||
blend_params=blend_params,
|
||||
)
|
||||
renderer = MeshRenderer(rasterizer=rasterizer, shader=shader)
|
||||
images = renderer(sphere_mesh)
|
||||
filename = "simple_sphere_light_%s%s.png" % (name, postfix)
|
||||
image_ref = load_rgb_image("test_%s" % filename, DATA_DIR)
|
||||
phong_renderer = MeshRenderer(rasterizer=rasterizer, shader=phong_shader)
|
||||
images = phong_renderer(sphere_mesh, lights=lights)
|
||||
rgb = images[0, ..., :3].squeeze().cpu()
|
||||
|
||||
if DEBUG:
|
||||
filename = "DEBUG_%s" % filename
|
||||
filename = "DEBUG_simple_sphere_dark%s%s.png" % (
|
||||
postfix,
|
||||
cam_type.__name__,
|
||||
)
|
||||
Image.fromarray((rgb.numpy() * 255).astype(np.uint8)).save(
|
||||
DATA_DIR / filename
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.assertClose(rgb, image_ref, atol=0.05)
|
||||
|
||||
########################################################
|
||||
# Move the light to the +z axis in world space so it is
|
||||
# behind the sphere. Note that +Z is in, +Y up,
|
||||
# +X left for both world and camera space.
|
||||
########################################################
|
||||
lights.location[..., 2] = -2.0
|
||||
phong_shader = HardPhongShader(
|
||||
lights=lights,
|
||||
cameras=cameras,
|
||||
materials=materials,
|
||||
blend_params=blend_params,
|
||||
)
|
||||
phong_renderer = MeshRenderer(rasterizer=rasterizer, shader=phong_shader)
|
||||
images = phong_renderer(sphere_mesh, lights=lights)
|
||||
rgb = images[0, ..., :3].squeeze().cpu()
|
||||
if DEBUG:
|
||||
filename = "DEBUG_simple_sphere_dark%s.png" % postfix
|
||||
Image.fromarray((rgb.numpy() * 255).astype(np.uint8)).save(
|
||||
DATA_DIR / filename
|
||||
image_ref_phong_dark = load_rgb_image(
|
||||
"test_simple_sphere_dark%s%s.png" % (postfix, cam_type.__name__),
|
||||
DATA_DIR,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Load reference image
|
||||
image_ref_phong_dark = load_rgb_image(
|
||||
"test_simple_sphere_dark%s.png" % postfix, DATA_DIR
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.assertClose(rgb, image_ref_phong_dark, atol=0.05)
|
||||
self.assertClose(rgb, image_ref_phong_dark, atol=0.05)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_simple_sphere_elevated_camera(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@@ -142,6 +165,60 @@ class TestRenderMeshes(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.test_simple_sphere(elevated_camera=True)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_simple_sphere_screen(self):
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Test output when rendering with PerspectiveCameras & OrthographicCameras
|
||||
in NDC vs screen space.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
device = torch.device("cuda:0")
|
||||
|
||||
# Init mesh
|
||||
sphere_mesh = ico_sphere(5, device)
|
||||
verts_padded = sphere_mesh.verts_padded()
|
||||
faces_padded = sphere_mesh.faces_padded()
|
||||
feats = torch.ones_like(verts_padded, device=device)
|
||||
textures = TexturesVertex(verts_features=feats)
|
||||
sphere_mesh = Meshes(verts=verts_padded, faces=faces_padded, textures=textures)
|
||||
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(2.7, 0.0, 0.0)
|
||||
|
||||
# Init shader settings
|
||||
materials = Materials(device=device)
|
||||
lights = PointLights(device=device)
|
||||
lights.location = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, +2.0], device=device)[None]
|
||||
|
||||
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(
|
||||
image_size=512, blur_radius=0.0, faces_per_pixel=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
for cam_type in (PerspectiveCameras, OrthographicCameras):
|
||||
cameras = cam_type(
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
R=R,
|
||||
T=T,
|
||||
principal_point=((256.0, 256.0),),
|
||||
focal_length=((256.0, 256.0),),
|
||||
image_size=((512, 512),),
|
||||
)
|
||||
rasterizer = MeshRasterizer(
|
||||
cameras=cameras, raster_settings=raster_settings
|
||||
)
|
||||
blend_params = BlendParams(1e-4, 1e-4, (0, 0, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
shader = HardPhongShader(
|
||||
lights=lights,
|
||||
cameras=cameras,
|
||||
materials=materials,
|
||||
blend_params=blend_params,
|
||||
)
|
||||
renderer = MeshRenderer(rasterizer=rasterizer, shader=shader)
|
||||
images = renderer(sphere_mesh)
|
||||
rgb = images[0, ..., :3].squeeze().cpu()
|
||||
filename = "test_simple_sphere_light_phong_%s.png" % cam_type.__name__
|
||||
|
||||
image_ref = load_rgb_image(filename, DATA_DIR)
|
||||
self.assertClose(rgb, image_ref, atol=0.05)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_simple_sphere_batched(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Test a mesh with vertex textures can be extended to form a batch, and
|
||||
@@ -165,7 +242,7 @@ class TestRenderMeshes(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
elev = torch.zeros_like(dist)
|
||||
azim = torch.zeros_like(dist)
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(dist, elev, azim)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(
|
||||
image_size=512, blur_radius=0.0, faces_per_pixel=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -193,12 +270,16 @@ class TestRenderMeshes(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
renderer = MeshRenderer(rasterizer=rasterizer, shader=shader)
|
||||
images = renderer(sphere_meshes)
|
||||
image_ref = load_rgb_image(
|
||||
"test_simple_sphere_light_%s.png" % name, DATA_DIR
|
||||
"test_simple_sphere_light_%s_%s.png" % (name, type(cameras).__name__),
|
||||
DATA_DIR,
|
||||
)
|
||||
for i in range(batch_size):
|
||||
rgb = images[i, ..., :3].squeeze().cpu()
|
||||
if i == 0 and DEBUG:
|
||||
filename = "DEBUG_simple_sphere_batched_%s.png" % name
|
||||
filename = "DEBUG_simple_sphere_batched_%s_%s.png" % (
|
||||
name,
|
||||
type(cameras).__name__,
|
||||
)
|
||||
Image.fromarray((rgb.numpy() * 255).astype(np.uint8)).save(
|
||||
DATA_DIR / filename
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -209,8 +290,6 @@ class TestRenderMeshes(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
Test silhouette blending. Also check that gradient calculation works.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
device = torch.device("cuda:0")
|
||||
ref_filename = "test_silhouette.png"
|
||||
image_ref_filename = DATA_DIR / ref_filename
|
||||
sphere_mesh = ico_sphere(5, device)
|
||||
verts, faces = sphere_mesh.get_mesh_verts_faces(0)
|
||||
sphere_mesh = Meshes(verts=[verts], faces=[faces])
|
||||
@@ -225,32 +304,45 @@ class TestRenderMeshes(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
# Init rasterizer settings
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(2.7, 0, 0)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
for cam_type in (
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
FoVOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
PerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
OrthographicCameras,
|
||||
):
|
||||
cameras = cam_type(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
|
||||
# Init renderer
|
||||
renderer = MeshRenderer(
|
||||
rasterizer=MeshRasterizer(cameras=cameras, raster_settings=raster_settings),
|
||||
shader=SoftSilhouetteShader(blend_params=blend_params),
|
||||
)
|
||||
images = renderer(sphere_mesh)
|
||||
alpha = images[0, ..., 3].squeeze().cpu()
|
||||
if DEBUG:
|
||||
Image.fromarray((alpha.numpy() * 255).astype(np.uint8)).save(
|
||||
DATA_DIR / "DEBUG_silhouette.png"
|
||||
# Init renderer
|
||||
renderer = MeshRenderer(
|
||||
rasterizer=MeshRasterizer(
|
||||
cameras=cameras, raster_settings=raster_settings
|
||||
),
|
||||
shader=SoftSilhouetteShader(blend_params=blend_params),
|
||||
)
|
||||
images = renderer(sphere_mesh)
|
||||
alpha = images[0, ..., 3].squeeze().cpu()
|
||||
if DEBUG:
|
||||
filename = os.path.join(
|
||||
DATA_DIR, "DEBUG_%s_silhouette.png" % (cam_type.__name__)
|
||||
)
|
||||
Image.fromarray((alpha.detach().numpy() * 255).astype(np.uint8)).save(
|
||||
filename
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with Image.open(image_ref_filename) as raw_image_ref:
|
||||
image_ref = torch.from_numpy(np.array(raw_image_ref))
|
||||
ref_filename = "test_%s_silhouette.png" % (cam_type.__name__)
|
||||
image_ref_filename = DATA_DIR / ref_filename
|
||||
with Image.open(image_ref_filename) as raw_image_ref:
|
||||
image_ref = torch.from_numpy(np.array(raw_image_ref))
|
||||
|
||||
image_ref = image_ref.to(dtype=torch.float32) / 255.0
|
||||
self.assertClose(alpha, image_ref, atol=0.055)
|
||||
image_ref = image_ref.to(dtype=torch.float32) / 255.0
|
||||
self.assertClose(alpha, image_ref, atol=0.055)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check grad exist
|
||||
verts.requires_grad = True
|
||||
sphere_mesh = Meshes(verts=[verts], faces=[faces])
|
||||
images = renderer(sphere_mesh)
|
||||
images[0, ...].sum().backward()
|
||||
self.assertIsNotNone(verts.grad)
|
||||
# Check grad exist
|
||||
verts.requires_grad = True
|
||||
sphere_mesh = Meshes(verts=[verts], faces=[faces])
|
||||
images = renderer(sphere_mesh)
|
||||
images[0, ...].sum().backward()
|
||||
self.assertIsNotNone(verts.grad)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_texture_map(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@@ -274,7 +366,7 @@ class TestRenderMeshes(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
# Init rasterizer settings
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(2.7, 0, 0)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
|
||||
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(
|
||||
image_size=512, blur_radius=0.0, faces_per_pixel=1
|
||||
@@ -337,7 +429,7 @@ class TestRenderMeshes(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
##########################################
|
||||
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(2.7, 0, 180)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
|
||||
# Move light to the front of the cow in world space
|
||||
lights.location = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, -2.0], device=device)[None]
|
||||
@@ -367,7 +459,7 @@ class TestRenderMeshes(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
# Add blurring to rasterization
|
||||
#################################
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(2.7, 0, 180)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
blend_params = BlendParams(sigma=5e-4, gamma=1e-4)
|
||||
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(
|
||||
image_size=512,
|
||||
@@ -429,7 +521,7 @@ class TestRenderMeshes(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
# Init rasterizer settings
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(2.7, 0.0, 0.0)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(
|
||||
image_size=512, blur_radius=0.0, faces_per_pixel=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -490,7 +582,7 @@ class TestRenderMeshes(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
# Init rasterizer settings
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(2.7, 0, 0)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
|
||||
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(
|
||||
image_size=512, blur_radius=0.0, faces_per_pixel=1, cull_backfaces=True
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,8 +14,8 @@ import torch
|
||||
from common_testing import TestCaseMixin, load_rgb_image
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import (
|
||||
OpenGLOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
OpenGLPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
FoVOrthographicCameras,
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
look_at_view_transform,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer.points import (
|
||||
@@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ class TestRenderPoints(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
points=verts_padded, features=torch.ones_like(verts_padded)
|
||||
)
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(2.7, 0.0, 0.0)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
raster_settings = PointsRasterizationSettings(
|
||||
image_size=256, radius=5e-2, points_per_pixel=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -97,7 +97,7 @@ class TestRenderPoints(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
point_cloud = Pointclouds(points=[verts], features=[rgb_feats])
|
||||
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(20, 10, 0)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLOrthographicCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T, znear=0.01)
|
||||
cameras = FoVOrthographicCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T, znear=0.01)
|
||||
|
||||
raster_settings = PointsRasterizationSettings(
|
||||
# Set image_size so it is not a multiple of 16 (min bin_size)
|
||||
@@ -150,7 +150,7 @@ class TestRenderPoints(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
batch_size = 20
|
||||
pointclouds = pointclouds.extend(batch_size)
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(2.7, 0.0, 0.0)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
|
||||
raster_settings = PointsRasterizationSettings(
|
||||
image_size=256, radius=5e-2, points_per_pixel=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ from common_testing import TestCaseMixin, load_rgb_image
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from pytorch3d.datasets import ShapeNetCore, collate_batched_meshes
|
||||
from pytorch3d.renderer import (
|
||||
OpenGLPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
FoVPerspectiveCameras,
|
||||
PointLights,
|
||||
RasterizationSettings,
|
||||
look_at_view_transform,
|
||||
@@ -174,7 +174,7 @@ class TestShapenetCore(TestCaseMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
# Rendering settings.
|
||||
R, T = look_at_view_transform(1.0, 1.0, 90)
|
||||
cameras = OpenGLPerspectiveCameras(R=R, T=T, device=device)
|
||||
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(R=R, T=T, device=device)
|
||||
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(image_size=512)
|
||||
lights = PointLights(
|
||||
location=torch.tensor([0.0, 1.0, -2.0], device=device)[None],
|
||||
|
||||